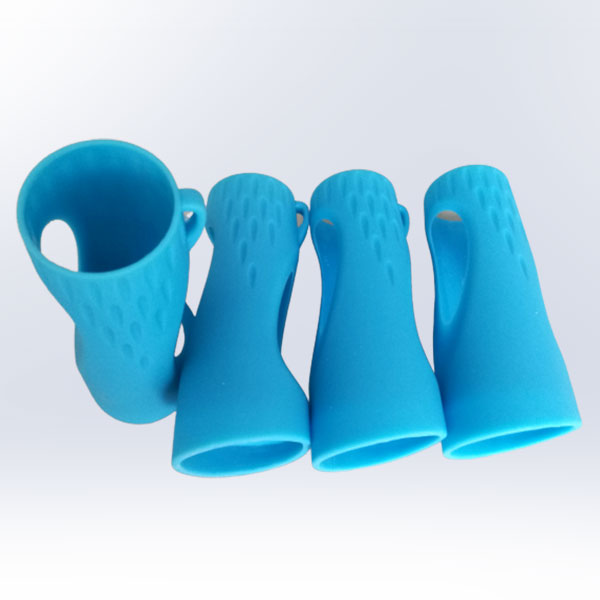
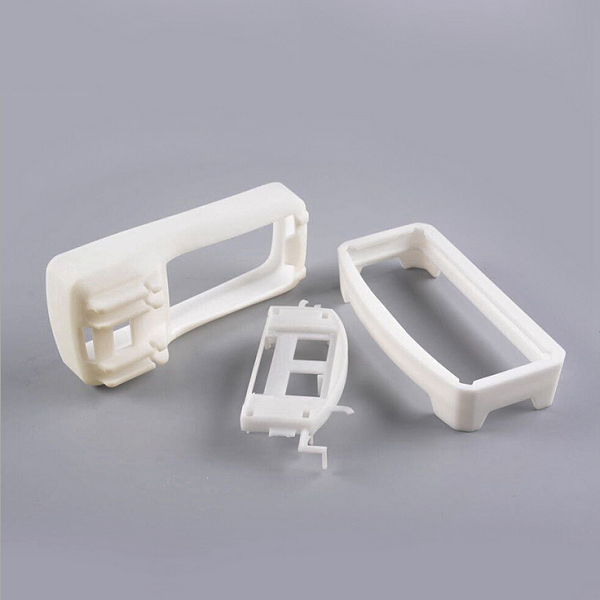
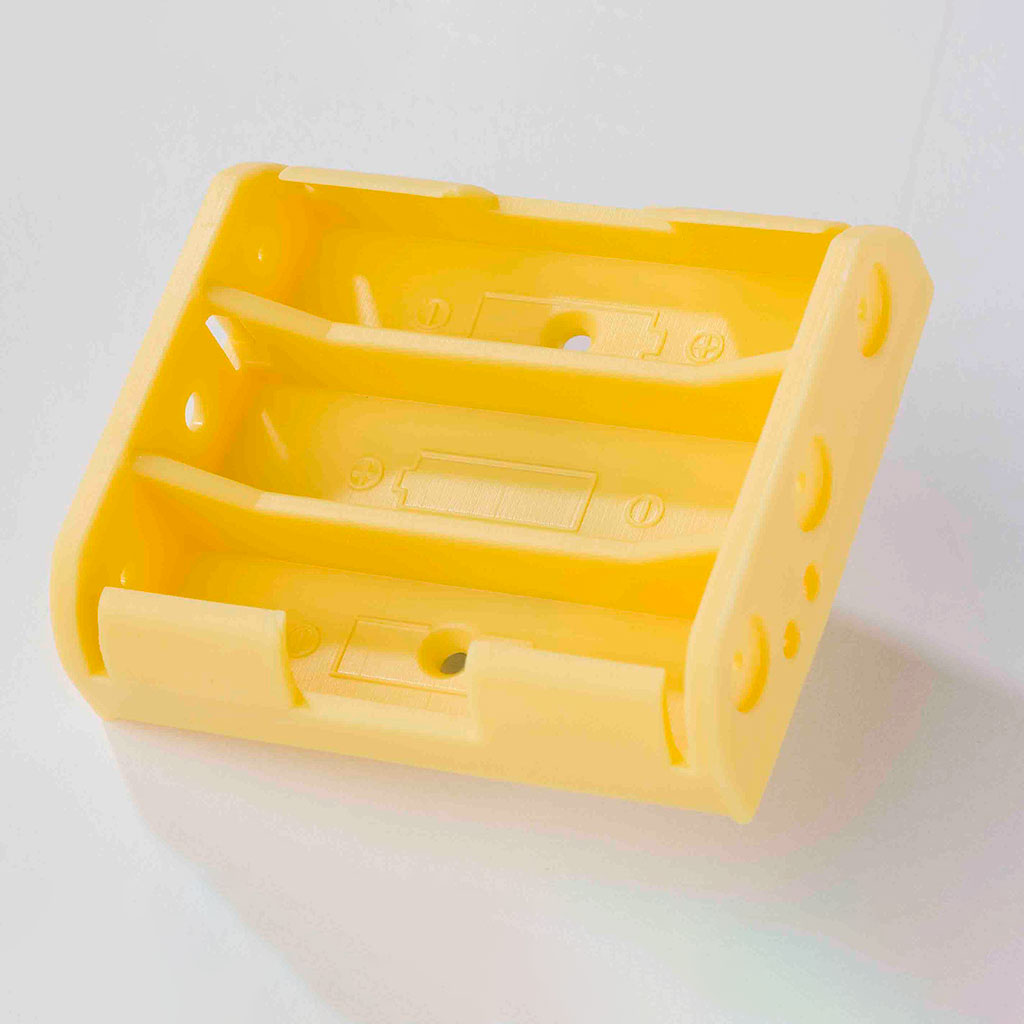
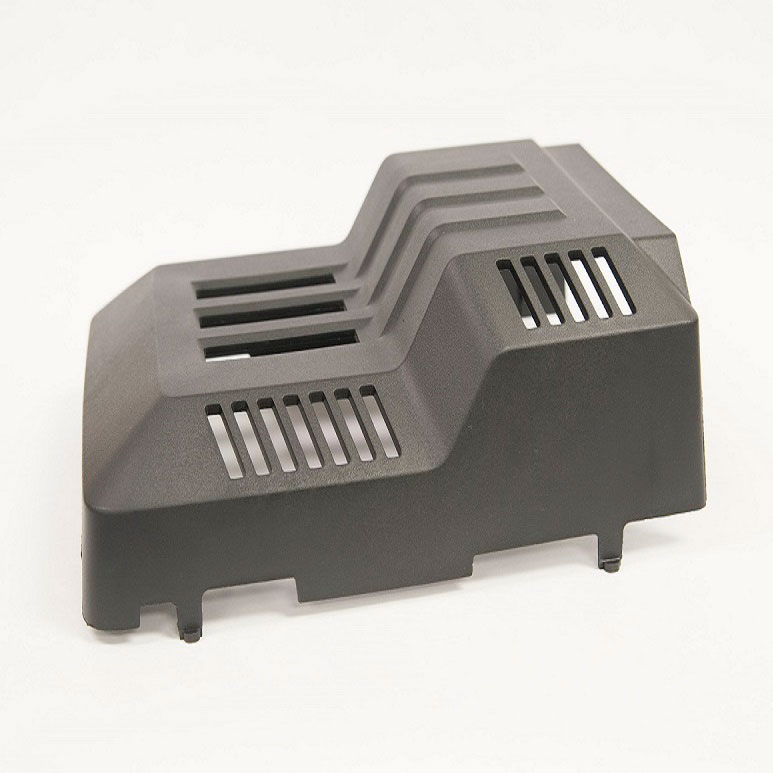
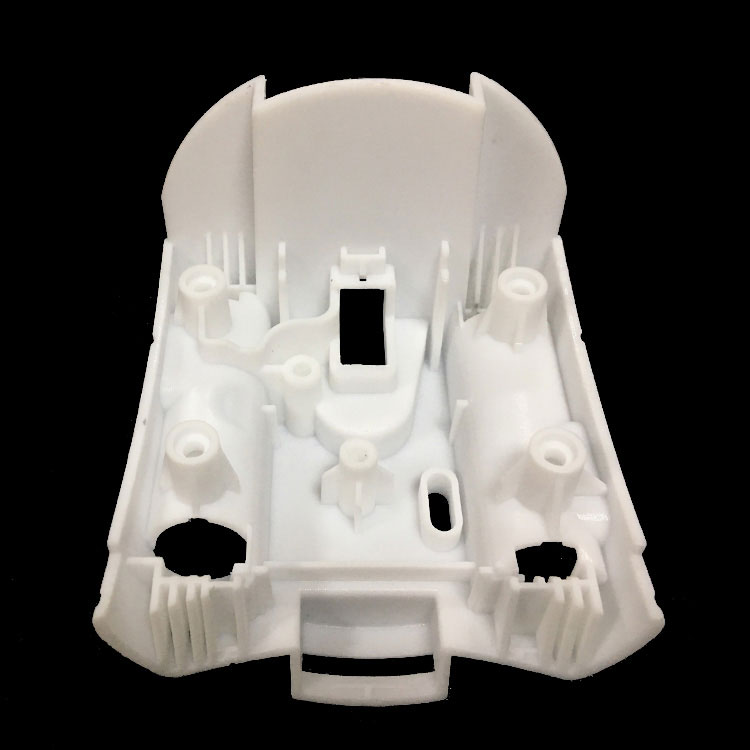
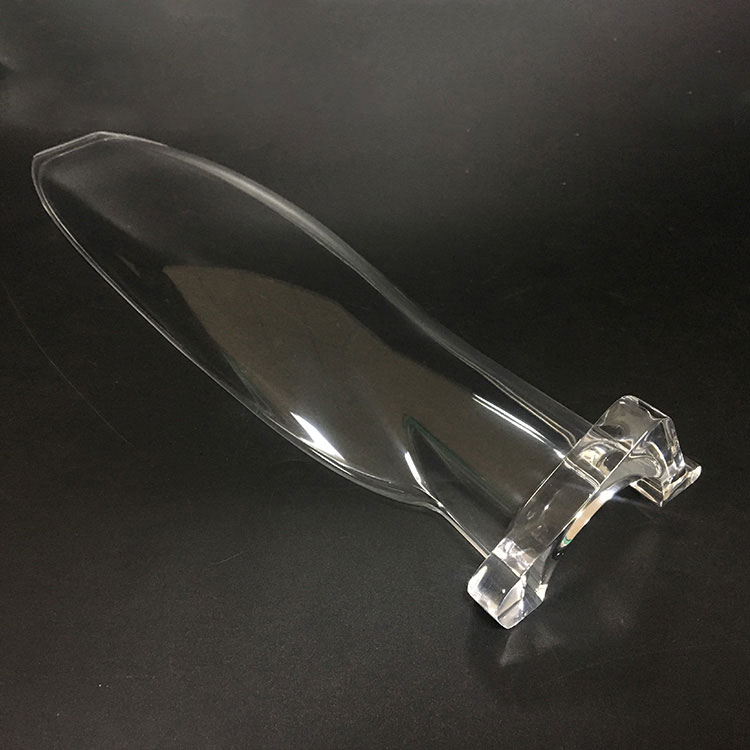
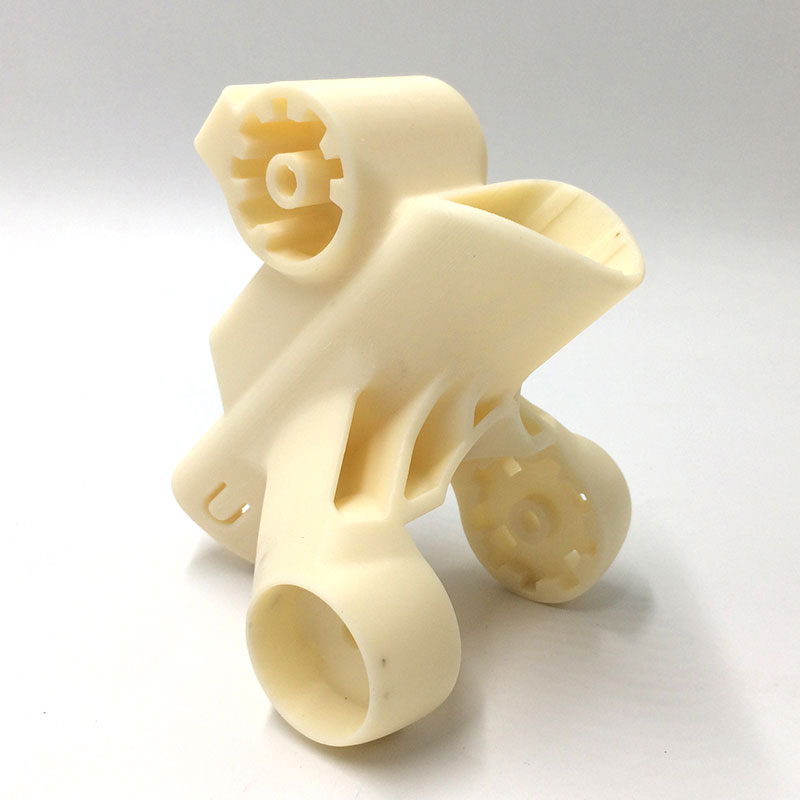
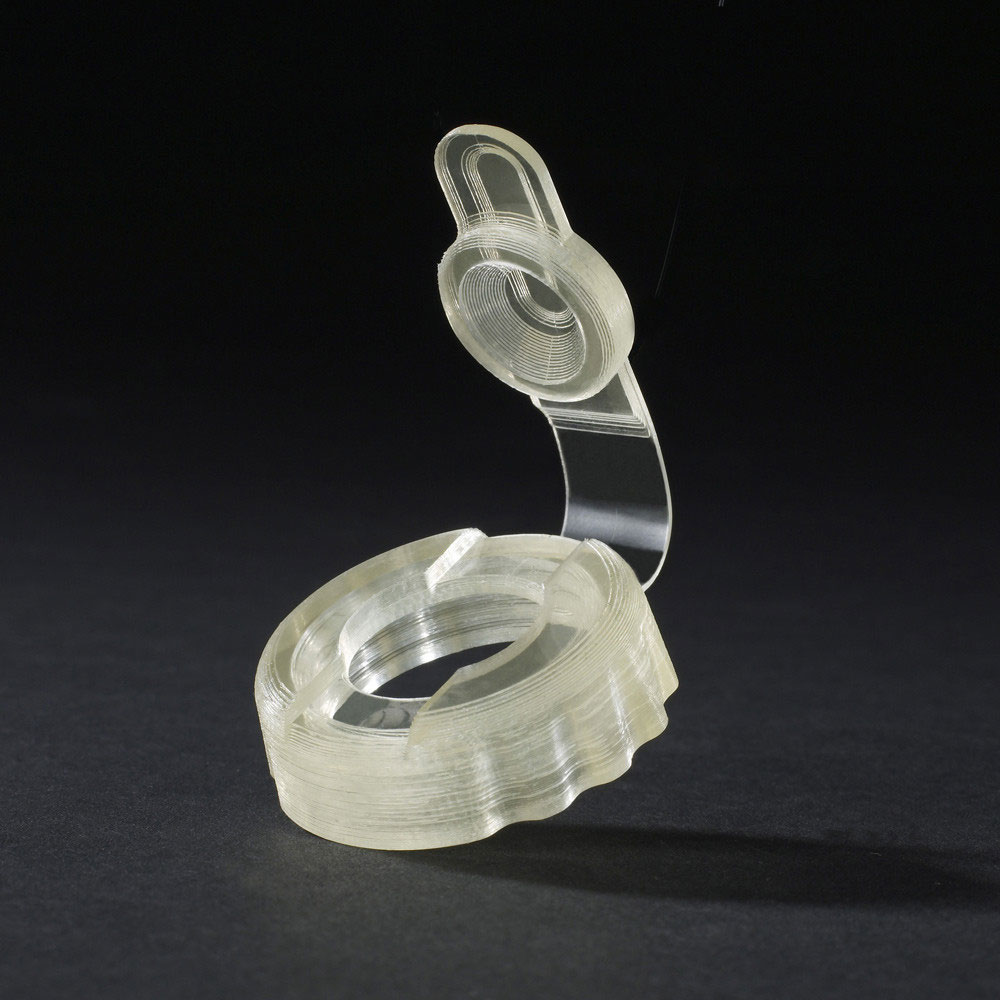
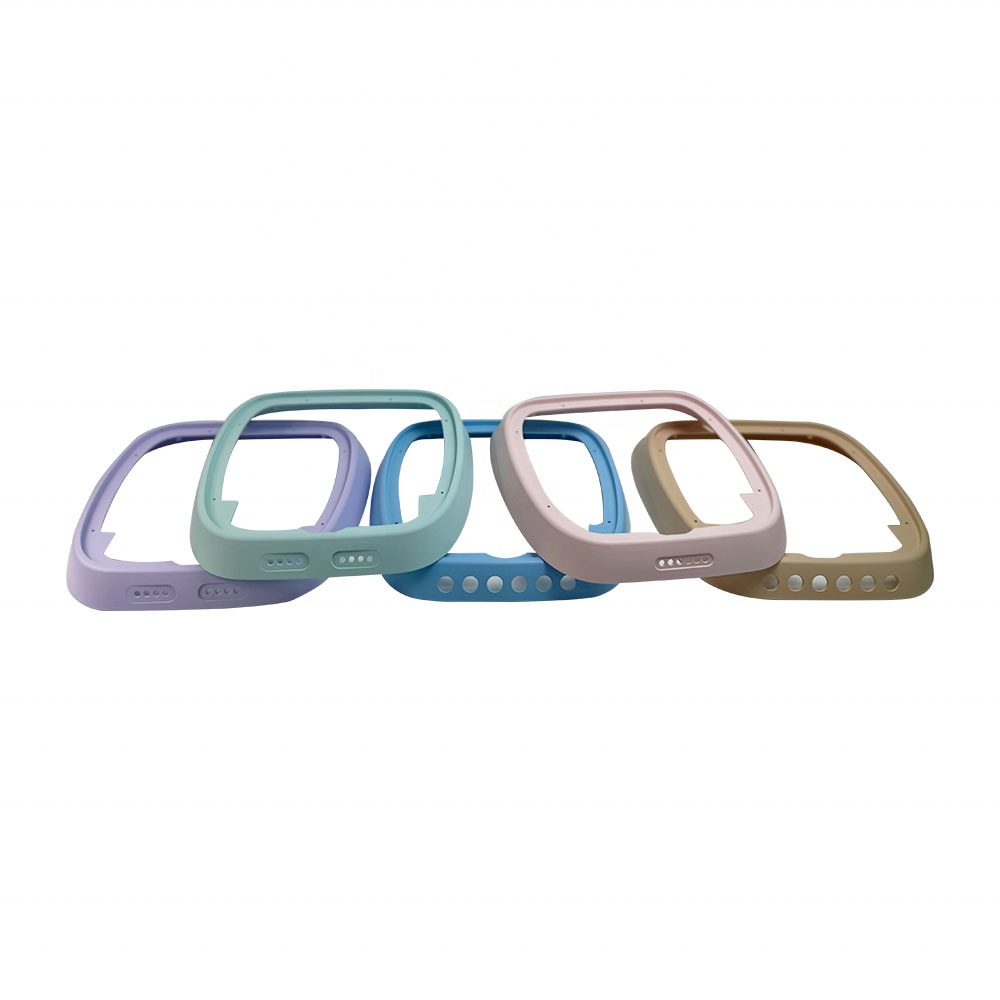
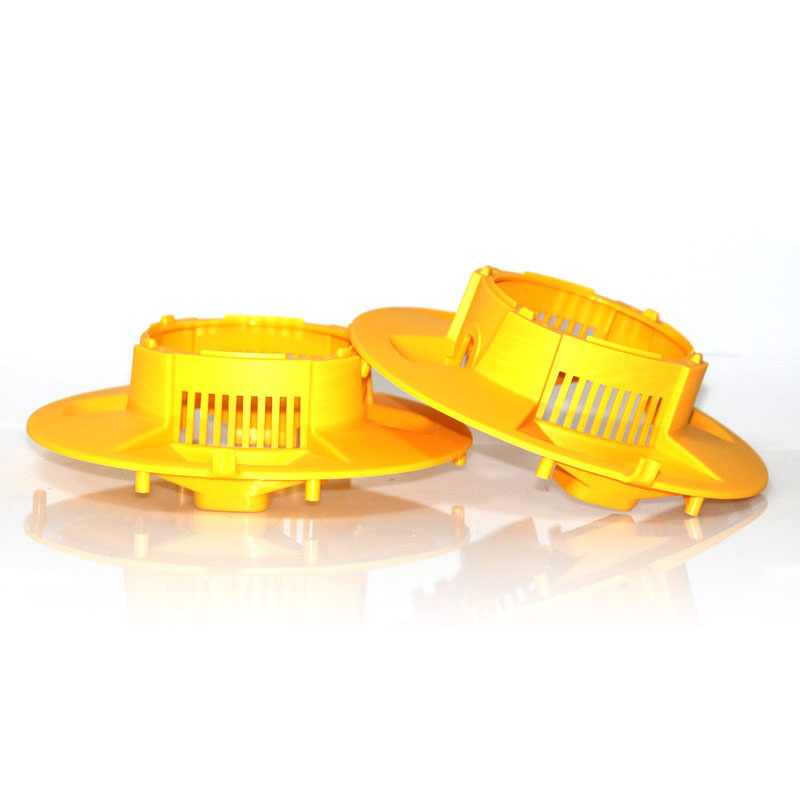
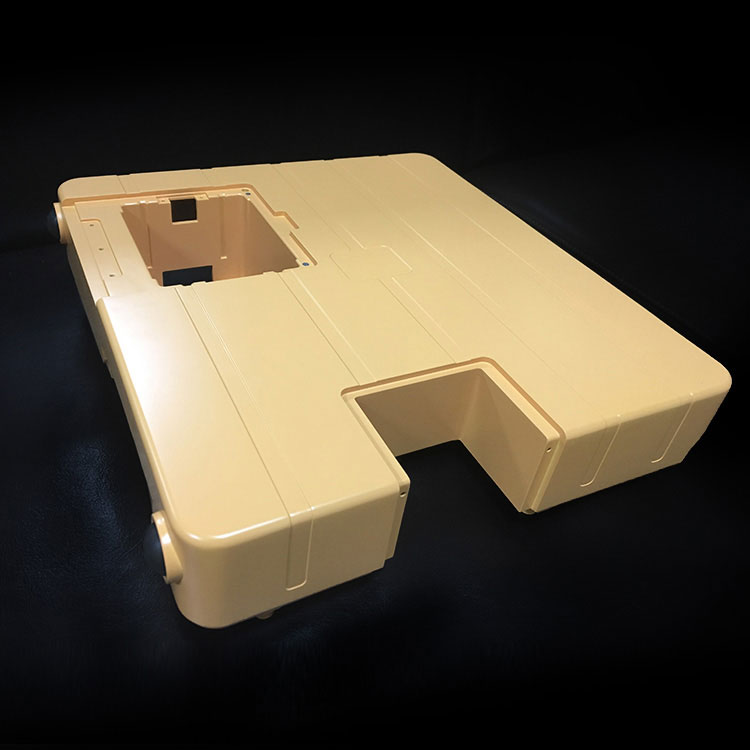
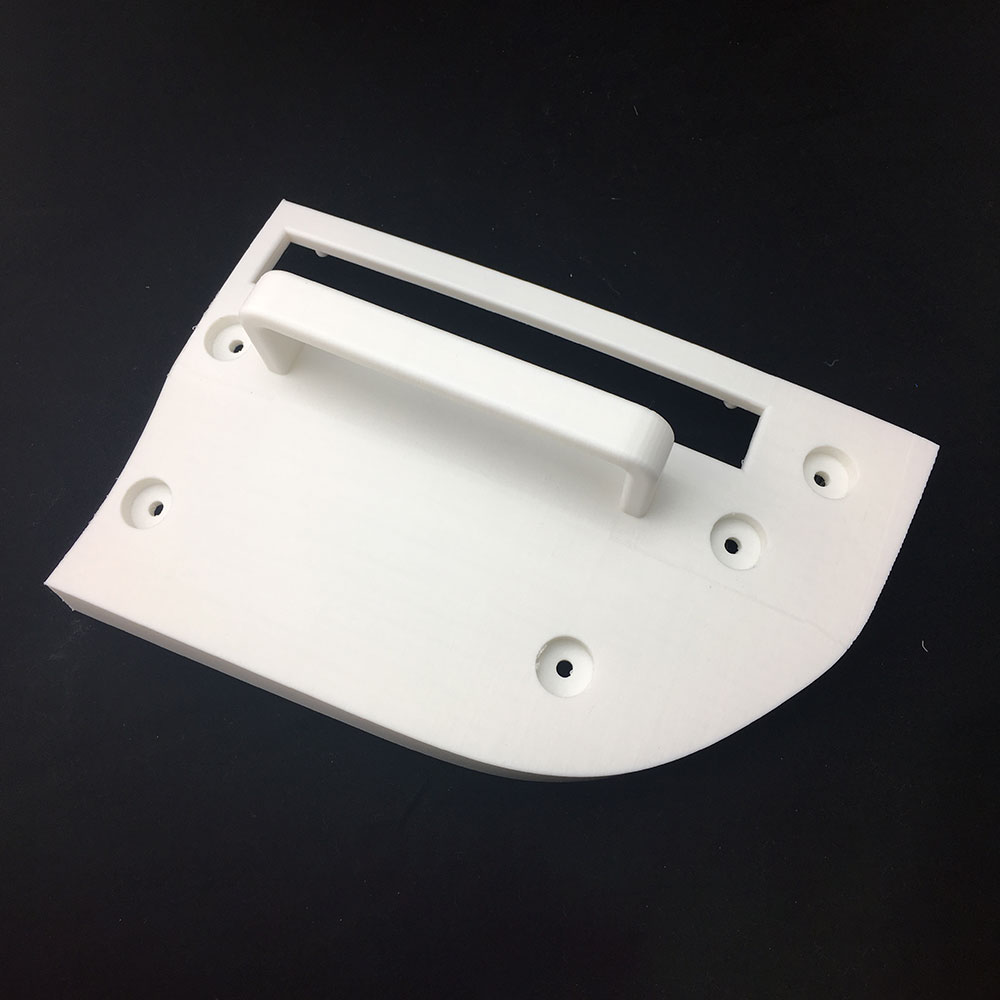
Your Trusted Partner for Rapid Prototyping Solutions
Holly specializes in custom OEM & ODM rapid prototyping, providing fast and precise injection molding solutions for industries such as automotive, electronics, medical, and consumer goods. Our advanced rapid tooling and injection molding techniques allow us to transform 3D CAD designs into functional prototypes within days.
With 40+ injection machines and a team of experienced engineers, we offer flexible production from small-batch prototypes to high-volume manufacturing. Using a variety of plastics and composite materials, we ensure high-quality prototypes that meet your performance and durability needs.
Our cost-effective and efficient prototyping services help you validate designs, test functionality, and accelerate time-to-market. Partner with Holly today for reliable, high-quality rapid prototyping solutions!
Explore Our Rapid Prototyping Capacities
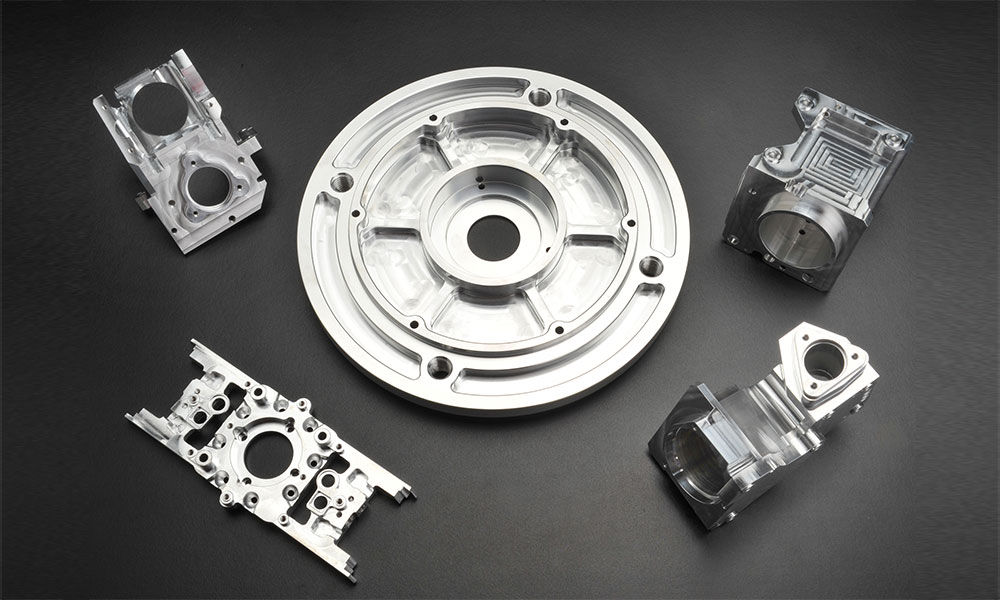
Holly offers comprehensive rapid prototyping solutions, ensuring fast, precise, and cost-effective production. Our capabilities include CNC machining (milling, turning, EDM), 3D printing (SLA, SLS, FDM), vacuum casting, and rapid injection molding, covering plastics and metals with ±0.05mm precision. We support functional prototypes, low-volume production, and multiple surface finishing options to meet diverse industry needs. With efficient workflows and fast turnaround times, we help accelerate product development from concept to production with high-quality, custom prototypes.
Rapid Prototyping Materials Available
| ABS
ABS (Acrylonitrile-Butadiene-Styrene) is a popular material for rapid prototyping due to its impact resistance, durability, and ease of processing. It is ideal for creating functional prototypes that require both strength and flexibility. In Rapid Prototyping, ABS is commonly used in industries like automotive, electronics, and consumer goods. For example, ABS is used for making automotive dashboards, electronic device housings, and appliance components, providing a high-strength and cost-effective solution for prototype testing and product development.
|
 |
| PLA
PLA (Polylactic Acid) is an excellent material for rapid prototyping due to its easy printability, low warping, and eco-friendly properties. It’s ideal for creating non-functional prototypes, mock-ups, and aesthetic models. In Rapid Prototyping, PLA is widely used in consumer products, architecture, and design prototypes. For example, it’s often used for visual models, concept prototypes, and 3D-printed models in product design due to its smooth finish and fast production time.
|
 |
| Nylon
Nylon is ideal for rapid prototyping due to its high strength, flexibility, and abrasion resistance. It’s excellent for producing functional prototypes that require durability and flexibility. In Rapid Prototyping, Nylon is widely used in industries such as automotive, aerospace, and consumer products. For example, it’s commonly used for gears, housing components, and snap-fit parts, offering great wear resistance and the ability to withstand mechanical stress during testing.
|
 |
| PE
Polyethylene (PE) is well-suited for rapid prototyping due to its low cost, chemical resistance, and flexibility. It is ideal for creating functional prototypes and low-stress parts that require durability and ease of processing. In Rapid Prototyping, PE is commonly used in packaging, consumer goods, and medical devices. For example, it’s often used for bottles, piping systems, and protective covers, providing reliable, cost-effective prototypes for testing and development.
|
 |
| PC
Polycarbonate (PC) is an ideal material for rapid prototyping due to its high impact resistance, optical clarity, and heat tolerance. It is perfect for creating durable, transparent, or high-strength parts. In Rapid Prototyping, PC is commonly used in electronics, automotive, and medical industries. For example, it’s often used for transparent enclosures, lens covers, and protective shields, providing a robust and functional prototype with excellent clarity and strength.
|
 |
| Aluminum
Aluminum is ideal for rapid prototyping due to its lightweight, high strength, and excellent machinability. It’s perfect for creating durable, complex parts that require precision and strength. In Rapid Prototyping, Aluminum is widely used in aerospace, automotive, and electronics industries. For example, it’s used for engine components, heat sinks, and housing enclosures, providing prototypes that can withstand stress and offer accurate performance testing.
|
 |
| Stainless steel
Stainless steel is perfect for rapid prototyping due to its high strength, corrosion resistance, and durability. It’s ideal for creating functional prototypes that need to endure harsh conditions and maintain performance over time. In Rapid Prototyping, Stainless steel is commonly used in aerospace, medical devices, and industrial machinery. For example, it’s used for surgical tools, valves, and structural components, providing robust prototypes that closely mimic final production parts.
|
 |
| Titanium alloys
Titanium alloys are ideal for rapid prototyping due to their exceptional strength-to-weight ratio, corrosion resistance, and high heat tolerance. These properties make titanium alloys perfect for demanding applications where performance and durability are critical. In Rapid Prototyping, titanium alloys are widely used in aerospace, medical, and automotive industries. For example, they are used for aircraft components, implants, and high-performance engine parts, providing prototypes that simulate real-world performance under extreme conditions.
|
 |
| Resin
Resin is ideal for rapid prototyping due to its high precision, smooth surface finish, and ability to create complex geometries. It is commonly used in SLA (Stereolithography) and DLP (Digital Light Processing) 3D printing. Resin is perfect for creating detailed models, concept prototypes, and visual parts. For example, it’s widely used in jewelry design, consumer electronics, and medical models for its fine detail and smooth finish.
|
 |
| CFRP
Carbon Fiber Reinforced Plastics (CFRP) are perfect for rapid prototyping due to their high strength, lightweight nature, and rigidity. These materials provide excellent structural integrity while maintaining low weight, ideal for demanding applications. In Rapid Prototyping, CFRP is used in aerospace, automotive, and sports equipment industries. For example, it’s used for lightweight vehicle components, drone frames, and bike parts, offering prototypes that replicate final product performance while ensuring durability and performance testing.
|
 |
| Ceramics
Ceramics are ideal for rapid prototyping due to their high-temperature resistance, wear durability, and precision. These properties make ceramics suitable for applications that demand high strength and thermal stability. In Rapid Prototyping, Ceramics are commonly used in aerospace, electronics, and medical devices. For example, ceramic prototypes are used for engine components, medical implants, and electrical insulators, offering exceptional performance under extreme conditions while providing accurate, functional models for testing.
|
 |
| Silicone
Silicone is ideal for rapid prototyping due to its flexibility, high-temperature resistance, and moldability. It is perfect for creating soft-touch components, gaskets, and seals. Silicone can be quickly molded into intricate shapes, making it ideal for prototypes that require elasticity or durability. It is commonly used in automotive, medical devices, and consumer goods. For example, silicone is used for silicone rubber seals, phone cases, and medical prosthetics to test form, fit, and function.
|
 |
| Rubber
Rubber is well-suited for rapid prototyping due to its flexibility, durability, and impact resistance. It is ideal for producing soft-touch parts that need to withstand wear, compression, or stretching. In Rapid Prototyping, rubber is commonly used in automotive, consumer goods, and industrial applications. For example, rubber is used for gaskets, seals, and vibration dampeners, providing prototypes that simulate real-world performance under pressure and stress.
|
 |
Rapid Prototyping Finishing Options
| Name | Description | Can be Applied with |
|---|---|---|

Polishing |
Polishing can eliminate the surface roughness of 3D printing and improve the appearance and texture. | Resin, plastic, and metal |
|
Sanding |
Sanding can remove layer lines and imperfections in 3D printing to achieve delicate results. | FDM and SLA printing |

Bead Blasting |
Bead blasting creates a uniform matte finish, smoothing the surface and removing roughness. | Metal and plastic parts |

Anodizing |
Anodizing increases corrosion resistance and adds color to the surface, enhancing durability. | Aluminum parts |

Coating |
Coating adds a layer of protection, enhancing wear resistance, corrosion protection, or aesthetic appeal. | Plastic, metal, and ceramic parts |

Plating |
Plating adds a thin metallic layer on the surface for better appearance and corrosion protection. | Metal parts |
| Painting | Painting provides a colored or protective layer to the surface, enhancing appearance and durability. | Metal, plastic, and ceramic parts |
| Laser Etching | Laser etching uses a laser to engrave patterns or text onto the surface for fine details. | Metal, plastic, and ceramics |
| Heat Treatment | Heat treatment improves material strength, hardness, and heat resistance. | Metal parts |
| Varnishing | Varnishing applies a protective and glossy coating to the surface for improved durability and appearance. | Wood, plastic, and metal |
| Inkjet Printing | Inkjet printing adds detailed text, patterns, or logos to the surface. | Plastic, metal, and ceramics |
| Deburring | Deburring removes sharp edges or excess material from parts to create smoother surfaces. | Metal and plastic parts |
| Water Transfer Printing | Water transfer printing adds complex patterns or designs to the surface, often for decorative purposes. | Plastic, metal, and automotive parts |
Rapid Prototyping Manufacturer FAQ
Rapid Prototyping FAQ Guide
In the following guide, you will know everything about Rapid Prototyping.
Rapid prototyping can directly accept product design (CAD) data without preparing any molds, tools, and fixtures, and quickly manufacture new product samples, molds or models. Since 1995, Holly has been focusing on plastic prototyping service in China, we have a professional rapid prototyping team with more than 10 years of experience.
Here you can find a quick prototyping guide. Feel free to contact us with any other questions.
1. What is rapid prototyping?
Rapid prototyping (RP) or rapid prototyping manufacturing (RPM) technology refers to the general term for the rapid manufacturing of three-dimensional entities of arbitrarily complex shapes under the direct drive of CAD models. The technology was developed in the 1990s. For manufacturing enterprises, it serves as a key common technology for developing new products. It is conducive to promoting enterprise product innovation, shortening the development cycle of new products, and improving product competitiveness.
2. What are the advantages of rapid prototyping?
Rapid prototyping can directly accept product design (CAD) data without preparing any molds, tools, and fixtures, and quickly manufacture new product samples, molds or models. As a result, popularizing and applying RP technology can improve the quality of development, shorten the development cycle of new products, and reduce costs. From the traditional “removal method” to today’s “growth method”, from mold manufacturing to moldless manufacturing, this is the revolutionary significance of RP technology for manufacturing.
3. What are the characteristics of rapid prototyping?
Rapid prototyping technology discretizes complex three-dimensional processing of an entity into a series of layered processing, which greatly reduces the difficulty of processing, and has the following characteristics:
- The rapidity of the entire molding process is suitable for the modern and fierce product market.
- It can produce 3D entities of any complex shape.
- It is directly driven by the CAD model to achieve a high degree of integration of design and manufacturing. It is intuitive and easy to modify, providing a good design environment for perfect product design.
- As a result, no special fixtures, molds, or tools are required during the molding process, thus saving money and reducing production time.
- The high integration of technology is an inevitable product of the development of modern science and technology, and it is also an inevitable product of the comprehensive application of modern science and technology, with distinctive high-tech characteristics.
The above characteristics lead to rapid prototyping technology mainly suitable for new product development, mold and model design and manufacturing, complex shape parts manufacturing, rapid single-piece, small-batch parts manufacturing, shape design inspection, difficult-to-process material manufacturing, assembly inspection, and rapid reverse engineering.
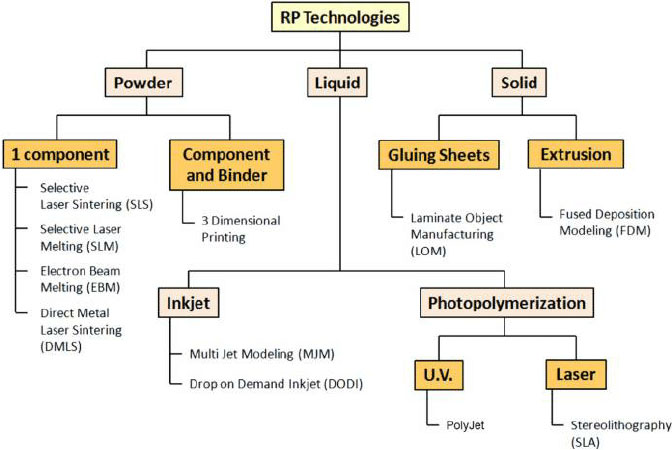
4. Types of Rapid prototyping?
3D printing technology is a collective term for a series of rapid prototyping technologies. The basic principle of 3D printing technology is lamination manufacturing. The rapid prototyping machine scans the cross-sectional shape of the product on the XY plane and intermittently moves the thickness of the layer on the Z coordinate, finally, a 3d part is formed. At present, rapid prototyping technology is divided into four types: Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM), 3DP Technology, Selective Laser Sintering (SLS), Stereo Lithography (SLA) and Laminate Manufacturing (LOM).
5. What is FDM technology for rapid prototyping?
Using filamentous hot-melt materials, FDM technology heats and melts the filaments together. At the same time, under the control of the computer, the three-dimensional spray head selectively coats the material on the worktable according to the cross-sectional profile information and forms a layer of cross-section after rapid cooling. After the formation of one layer is completed, the machine tool table is lowered by a height (that is, the layer thickness) to form the next layer until the entire solid shape is completed. There are many kinds of molding materials, and the strength and precision of molding parts are quite high. This technology is mainly applied to small plastic parts.
6. What is rapid prototyping SLS technology?
SLS technology is to first lay a layer of metal powder or non-metal powder material workbench, under computer control, let the solid part of the laser-sintered powder according to the interface configuration information, and finally continue to repeat the previous process to form a layer. This method has a simple manufacturing process, fast forming speed, low cost, and a wide range of material selections. It is mainly used in the casting industry to directly produce rapid molds.
7. What is SLA technology for rapid prototyping?
The SLA technology uses photosensitive resin as raw material and uses computer-controlled lasers to scan the surface of the liquid photosensitive resin point by point according to the layered cross-sectional information of the part. The resin thin layer in the scanning area is photopolymerized and cured to form the thin layer part. After the curing of one layer is completed, move the worktable down by a thickness of one layer, and then coat a new layer of liquid resin on the surface of the cured resin until a three-dimensional solid model is obtained. The method has fast forming speed, high dimensional accuracy, and a high degree of automation that can form any complex shape and is mainly used for rapid forming of complex and high-precision parts.
8. What is the difference between SLS and SLA technology for rapid prototyping?
There are 7 obvious differences between rapid prototyping SLS and SLA technology. Details are as follows:
1) Process principle
The process principle of SLS is to generate high temperature by laser, and the temperature of powder is raised to the melting point for sintering, while the process principle of SLA is to generate ultraviolet light by laser, which is irradiated on the surface of the material for curing.
2) Resolution rate
Building materials can be cured with laser beams in both technologies, but they use different wavelengths: ultraviolet light for SLA and infrared light for SLS. The corresponding strong irradiation area is also different, the ultraviolet light irradiation area is much smaller than the infrared light irradiation area. Therefore, in general, the resolution of SLA is higher than that of SLS.
3) Mechanical behaviour
SLS printers can use a variety of materials in powder form, the most common is nylon (PA12), its properties (such as colour, strength, elasticity, hardness, etc.) can be changed by additives. This material has excellent properties: durable and abrasion-resistant.
As for SLA printers, manufacturers usually use their own resin materials, and there are many third-party options to choose from, and the price is relatively cheap. Generally speaking, resin materials are harder than nylon, so they are weaker.
Another important difference is their performance under load: hard resin will become fragments under severe impact, while nylon has a certain degree of elasticity and can be restored to its original state.

4) Visible surface
The visible surface of the SLS printed product will form a solid material with pores because the air in the powder forms small bubbles on the sintered material, which will feel a little rough when in contact. And the surface of the object printed by SLA will be smoother.
In addition, nylon powder usually has three colours of black, white and grey, and the resin material can produce any colour through white or transparent resin and pigment.
5) Support structure
SLA printing technology requires a supporting structure. When using the support structure, the printed parts need to be cleaned manually, which takes a certain amount of time. It is important to keep in mind that the materials that are used in SLA printing should also be the same as those used in supporting materials. On the contrary, SLS printing technology is one of the few examples that does not require any support structure because the unsintered powder acts as the support structure during the printing process.
6) Post-processing
Although their printed products can be post-processed, there are still some differences. Before proceeding with post-processing, we should check with professional suppliers. For example, SLA printed parts do not require polishing.
7) Cost
As nylon is a common material, and SLS technology can handle a large volume of output, SLS is usually cheaper than SLA.
9. How does rapid prototyping work?
The basic principle of rapid prototyping technology is: to segment the three-dimensional data model in the computer to obtain the profile data of each layer. According to this information, the computer controls the laser (or nozzle) to cure the powder material (or solidify layer after layer of liquid photosensitive resin, or cut layer after layer of sheet material, or spray layer after layer of hot melt). Material or binder) selective sintering layer by layer. Then, the sheet-like entities are stacked layer by layer through fusion, polymerization, bonding, etc., and finally designed new product samples, models or molds are manufactured.
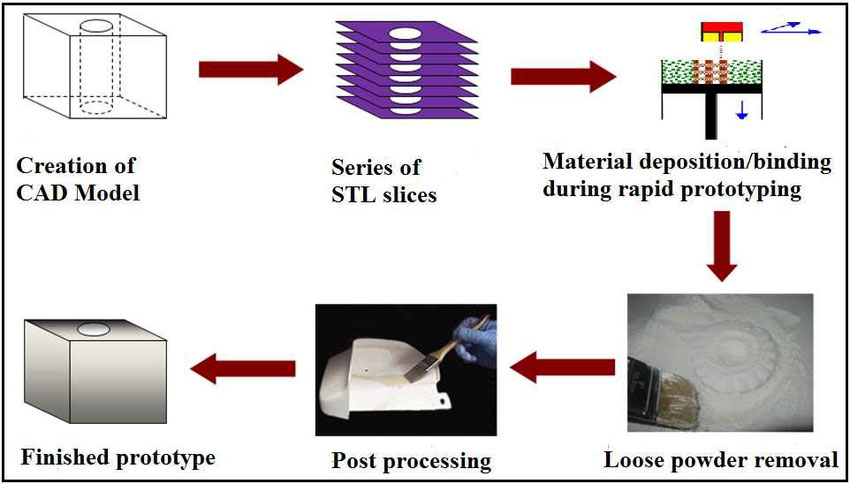
10. What are the advantages of plastic prototyping service SLA technology?
- As the earliest rapid prototyping technology, it has been highly developed.
- Production cycles are short and processing is fast.
- It can handle prototypes and molds with complex structures or difficult notifications.
- Visualize the CAD digital model to reduce maintenance costs.
- Provide test samples to verify and check the results of computer simulation calculations.
- It can be operated online and remotely controlled, which is conducive to production automation.
11. What are the advantages of SLS technology in rapid prototyping?
The most prominent advantage of SLS is that it can use a wide range of materials. In theory, any powder material that can form interatomic bonds after heating, including paraffin, polymers, metals, ceramic powders and their composite powder materials, can be used in SLS. Due to the wide variety of SLS molding materials, wide distribution of molding properties, material savings, and is suitable for multiple purposes, without the need to design and manufacture complex support structures, SLS has gained more and more popularity and wide applications today.
12. What is the process of rapid prototyping?
The rapid prototyping process includes: pre-processing (construction of the three-dimensional model, approximation of the three-dimensional model, and slice of the three-dimensional model), layered and superimposed manufacturing (cross-section and cross-section overlap) and post-processing (such as surface treatment, etc.) ).

13. What are the shortcomings of rapid prototyping SLA?
- The cost of the SLA system is relatively high, and the cost of use and maintenance is also relatively high.
- The SLA system is such sophisticated equipment that needs to be operated on liquids, and it needs a strict working environment.
- The material of the molded parts is mostly resin, which has limited strength, rigidity and heat resistance, and is not suitable for long-term storage.
- The preprocessing software and driving software have a large amount of calculation and are closely related to the processing effect.
- The software system is complicated to operate and difficult to learn. In addition, the file format it uses is not familiar to most designers.
14. What are the disadvantages of SLS for rapid prototyping?
1) Shrinkage rate of printed matter
Powder materials such as nylon shrink after sintering. Shrinkage is affected by various factors, including powder type, laser energy used for particle sintering, part shape, and cooling process. Note that the part does not shrink symmetrically in all directions.
2) The operation after printing is more complicated.
After the printing process, there is enough time to cool the powder, so we can remove the material blocks. Workers need to dig out parts from the material block, use a vacuum cleaner to remove excess powder or use the wind to remove remaining particles. After finishing all the work, it can be cured by heating to increase strength. In addition, sometimes it may take time to stain, frost, or paint the surface.
3) Discoloration/moisture absorption
If the printed part is to be dyed, painted or coated, its porous structure may absorb a large amount of dust, oil or water from the air, resulting in a colour change or some weight reduction.
4) Processing and material loss
15. How do we use rapid prototyping?
Rapid prototyping technology can be used for design evaluation and functional testing in the product development stage. In addition, it can also be used in household appliances, automobiles, toys, light industrial products, architectural models, medical equipment and artificial organ models, spacecraft, military equipment, archaeology, industrial manufacturing, sculpture and film production and other industries.
16. What is a rapid prototyping tool?
A rapid prototyping tool is a tool that uses its specific shape to form a product with a certain size, shape and surface accuracy. It is mainly used for mass production. Mass production reduces the cost of each product despite the high production and mold manufacturing costs.
17. What is the difference between 3D printing and rapid prototyping?
Rapid prototyping is a new type of molding technology based on the material accumulation method. This is considered a major achievement in the manufacturing industry in the past 20 years. By integrating mechanical engineering, CAD, reverse engineering technology, layered manufacturing technology, numerical control technology, material science, laser technology, etc., design ideas can be directly, accurately, automatically and quickly transformed into prototypes with certain functions or directly manufactured parts. This provides an efficient and low-cost method for realizing part prototyping and validating new design ideas.
3D printing technology refers to the latest rapid prototyping equipment using light-curing and paper lamination technology. This is basically the same as ordinary printing. The printer contains liquid or powder and other “printing materials.” After connecting the “printed materials” to the computer, they are superimposed through the computer control layer, and finally, the design in the computer becomes a real object.
18. Compared with mold manufacturing, what are the advantages of rapid prototyping?
Technology for rapid prototyping does not depend on the structure or shape of the product. As long as there is CAD data, no matter how complicated the shape and structure of the product are, it can be easily completed. Therefore, this technology is very suitable for OEM and ODM projects. Moreover, the use of rapid prototyping technology does not require opening new molds, which can reduce the cost of developing new products and shorten the cycle. In addition, most rapid prototyping equipment is available 24/7 without an operator, which helps to save labour costs and improve production efficiency.
Prototyping technology can also be used to design, develop, test, and manufacture small batches of products. Any project that requires physical proofing or testing can use rapid prototyping technology.
In addition, the amount of post-assisted processing of rapid prototyping technology is greatly reduced, and the time span of data leakage and outsourcing processing is avoided.
19. What is the significance of rapid prototyping?
First, rapid prototyping greatly shortens the development time for new products.
Second, it improves the possibility of manufacturing complex parts.
Third, it plays an important role in improving the first-time success rate of new product production. Because we can find design problems in time, and then make improvements to avoid big losses.
Fourth, we can carry out new product design, sample production, market promotion and production preparation at the same time.
Finally, it helps to save a lot of mold opening costs.
20. What can we do to improve rapid prototyping technology?
Rapid prototyping technology is widely used in the manufacturing industry (up to 67%), which shows that it plays an important role in improving the level of product design and manufacturing.
Rapid prototyping technology still has some shortcomings. In the future, we can improve rapid prototyping technology in the following areas:
- Improve the reliability, productivity and production capacity of the rapid prototyping system, especially the production accuracy;
- Develop economic rapid prototyping system;
- Improve and innovate rapid prototyping methods and processes;
- Application of rapid mold manufacturing;
- Develop rapid prototyping materials with good performance;
- Develop high-performance software for rapid prototyping.
- 1. What is rapid prototyping?
- 2. What are the advantages of rapid prototyping?
- 3. What are the characteristics of rapid prototyping?
- 4. Types of Rapid prototyping?
- 5. What is FDM technology for rapid prototyping?
- 6. What is rapid prototyping SLS technology?
- 7. What is SLA technology for rapid prototyping?
- 8. What is the difference between SLS and SLA technology for rapid prototyping?
- 9. How does rapid prototyping work?
- 10. What are the advantages of plastic prototyping service SLA technology?
- 11. What are the advantages of SLS technology in rapid prototyping?
- 12. What is the process of rapid prototyping?
- 13. What are the shortcomings of rapid prototyping SLA?
- 14. What are the disadvantages of SLS for rapid prototyping?
- 15. How do we use rapid prototyping?
- 16. What is a rapid prototyping tool?
- 17. What is the difference between 3D printing and rapid prototyping?
- 18. Compared with mold manufacturing, what are the advantages of rapid prototyping?
- 19. What is the significance of rapid prototyping?
- 20. What can we do to improve rapid prototyping technology?