Plastic Injection Molding Manufacturer and Supplier from China
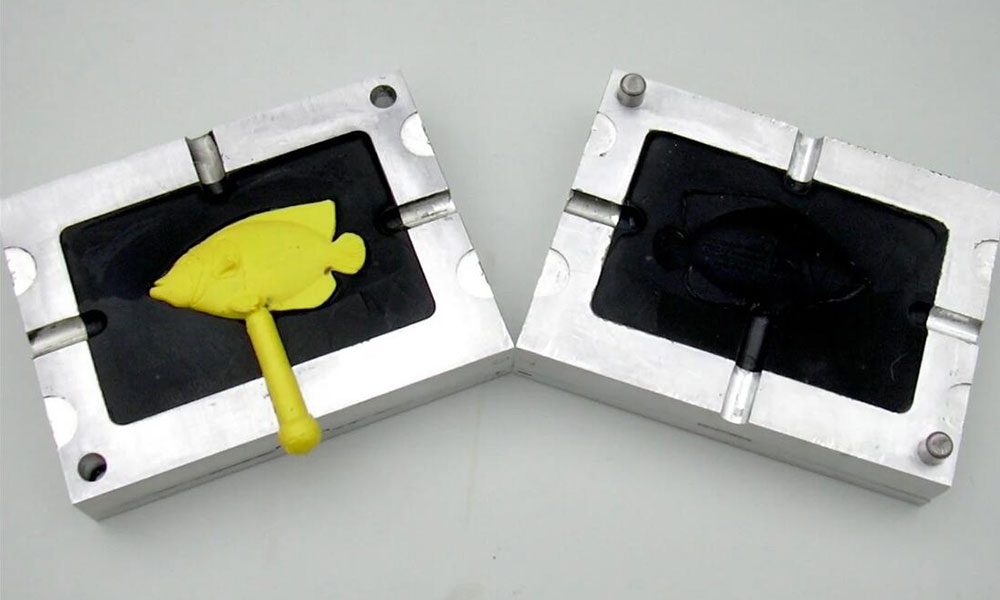
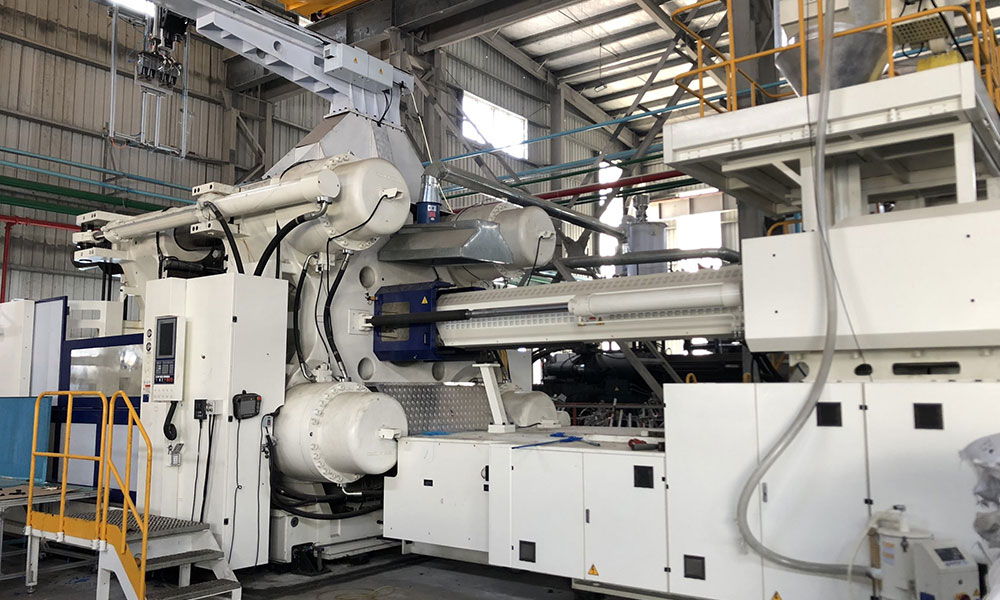
At Holly, we specialize in high-precision plastic injection molding, providing cost-effective, reliable, and scalable manufacturing solutions for industries such as automotive, medical, electronics, and consumer goods. Whether you need rapid prototyping or high-volume production, our state-of-the-art injection molding technology ensures superior quality and consistency in every part.
With a robust network of trusted suppliers and an ISO-certified production process, we offer a full range of services, including custom mold design, over-molding, insert molding, multi-cavity molding, and secondary finishing. Our commitment to precision engineering and strict quality control guarantees durable, high-performance plastic components that meet global standards.
Partner with Holly for efficient lead times, competitive pricing, and tailored injection molding solutions to bring your product vision to life.
Explore our Plastic Injection Molding Products
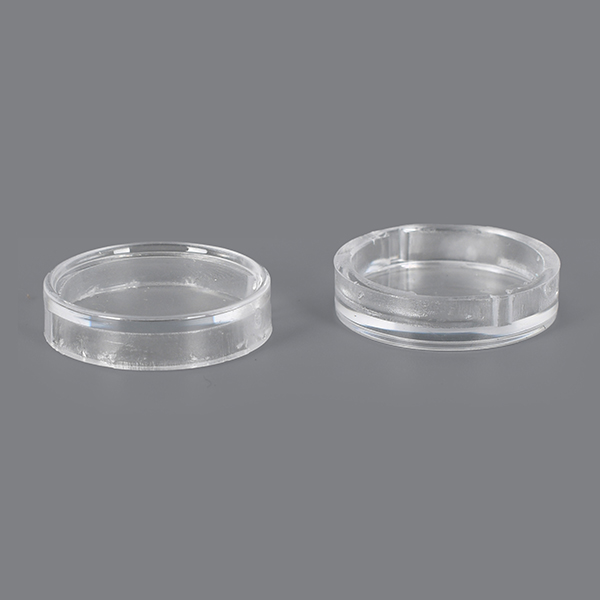
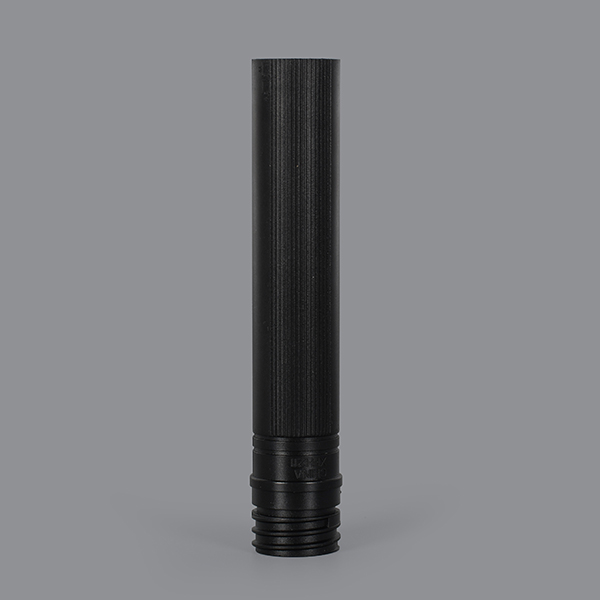
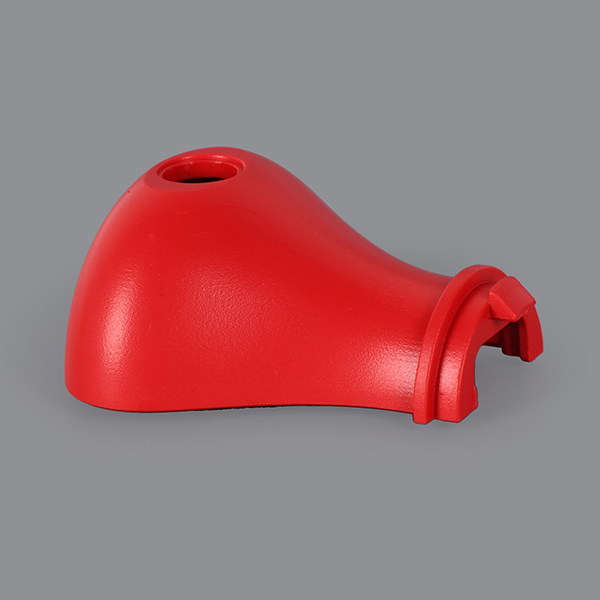
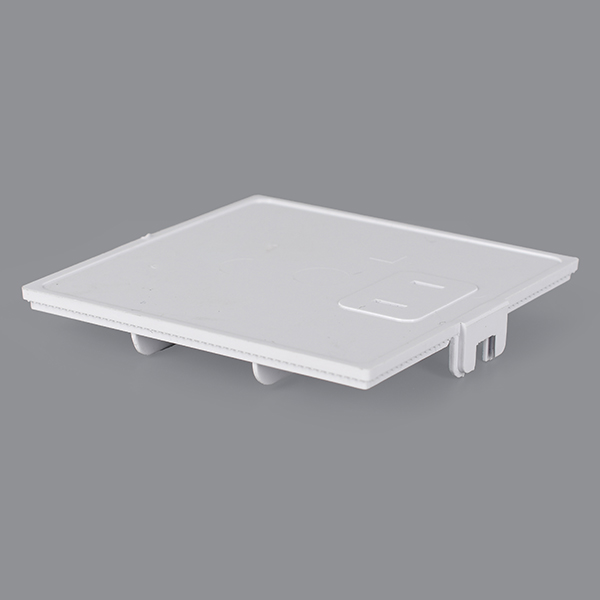
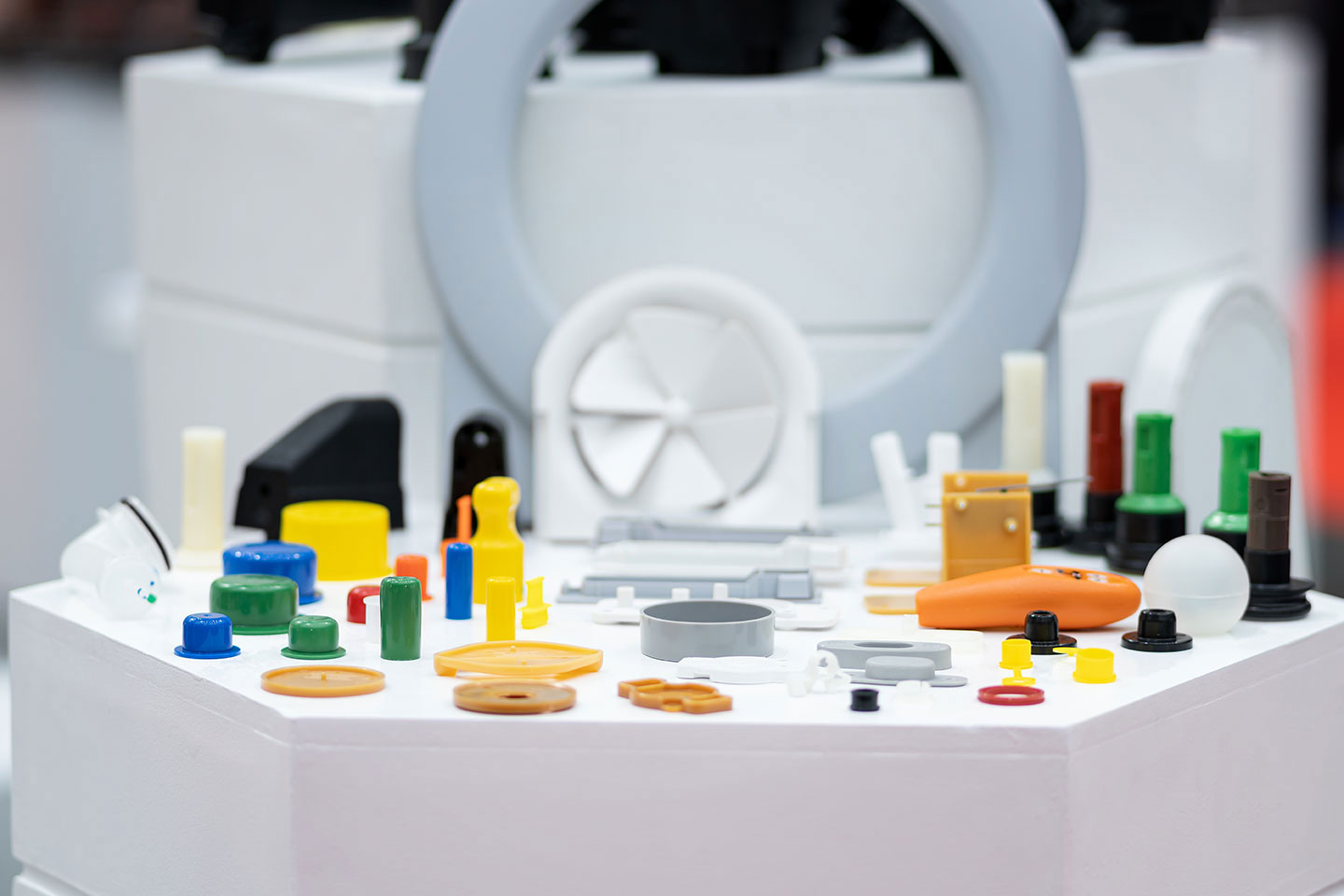
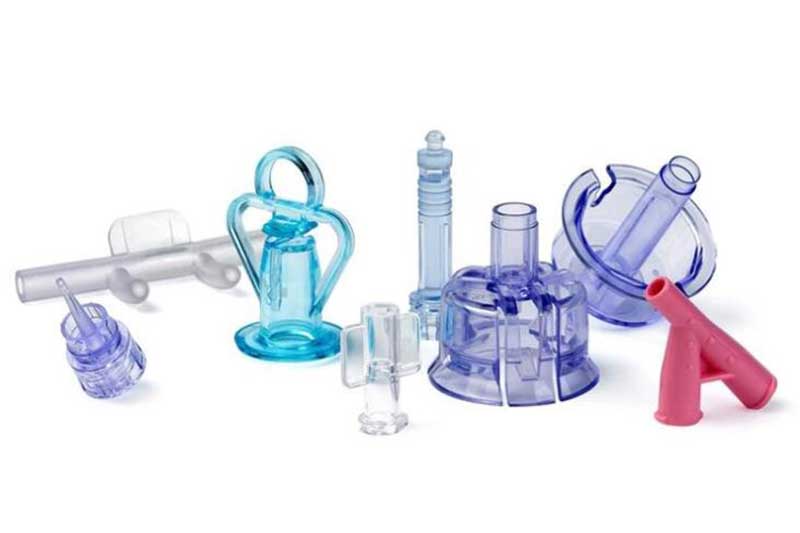
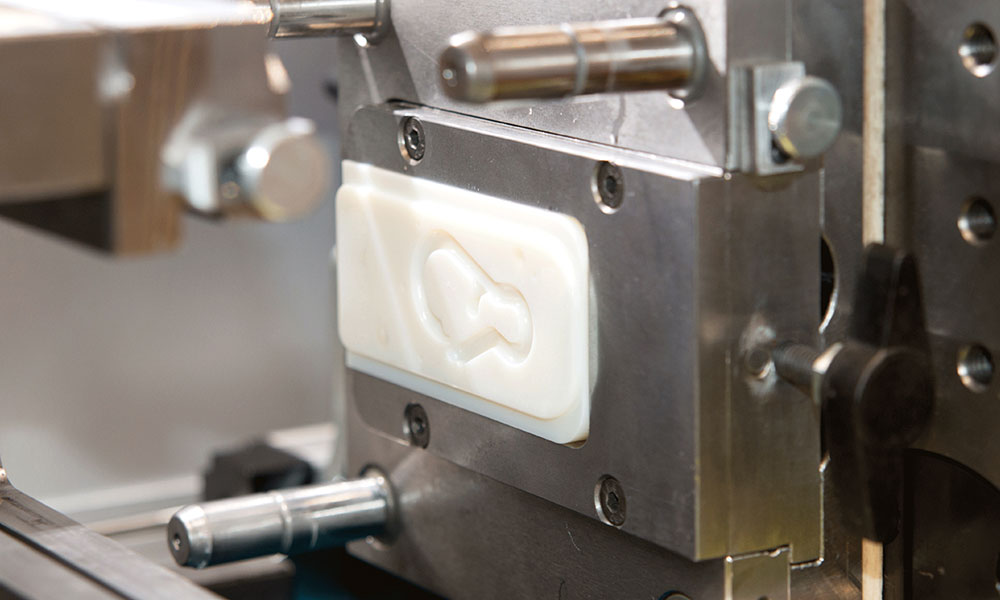
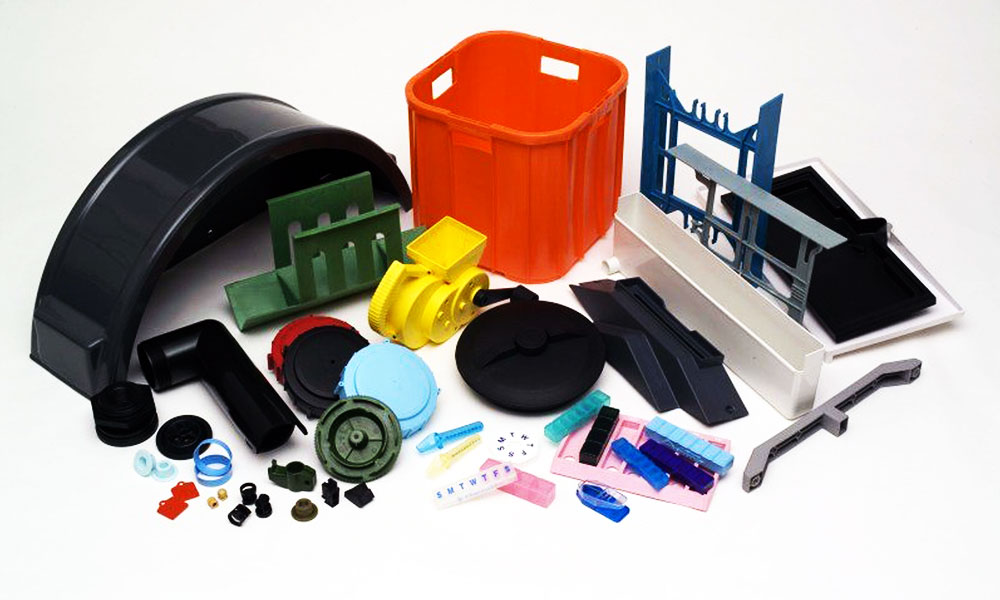
Holly offers a wide range of plastic injection molded products, catering to various industries and applications. Our product categories include automotive components, medical devices, consumer electronics casings, industrial enclosures, household appliance parts, and custom precision parts. Whether for high-strength structural applications, heat-resistant components, or intricate micro-molded parts, we provide tailored solutions with high-quality materials and precision engineering. No matter the complexity or performance requirements, we deliver reliable, cost-effective plastic injection molding solutions to meet your needs.
Plastic injection Molding Capabilities
Different types of Plastic Materials Available
| PP
PP (Polypropylene) is a lightweight and durable thermoplastic widely used in injection molding. It offers excellent chemical resistance, flexibility, and impact strength, making it ideal for automotive parts, medical devices, and consumer goods. PP is moisture-resistant, fatigue-resistant, and can be modified for improved heat stability or UV protection. It supports various finishing options and is perfect for cost-effective, high-volume production.
|
 |
| PE
PE (Polyethylene) is a durable and flexible thermoplastic widely used in injection molding for its excellent impact resistance, chemical stability, and moisture resistance. It is lightweight, has good electrical insulation properties, and is available in different densities (LDPE, HDPE) to suit various applications. PE is commonly used in packaging, automotive components, piping, and consumer goods. Its low cost, ease of processing, and recyclability make it a preferred material for both industrial and commercial products.
|
 |
| PS
PS (Polystyrene) is a rigid and lightweight thermoplastic widely used in injection molding due to its excellent clarity, ease of processing, and affordability. It offers good dimensional stability, electrical insulation, and chemical resistance, making it ideal for packaging, disposable containers, consumer electronics, and household products. PS is available in both general-purpose (GPPS) and high-impact (HIPS) variants, catering to different strength and flexibility requirements. Its cost-effectiveness and versatility make it a popular choice for various applications.
|
 |
| ABS
ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene) is a versatile thermoplastic widely used in injection molding due to its excellent impact resistance, toughness, and ease of processing. It offers good mechanical strength, heat resistance, and chemical stability, making it ideal for automotive parts, consumer electronics, and household appliances. ABS can also be easily painted, plated, or textured for enhanced aesthetics and functionality. Its cost-effectiveness and balanced properties make it a popular choice for durable plastic components.
|
 |
| PC
PC (Polycarbonate) is a high-strength thermoplastic known for its exceptional impact resistance, optical clarity, and heat resistance. It offers excellent dimensional stability, flame retardancy, and UV resistance, making it ideal for automotive components, electronic housings, medical devices, and transparent applications like lenses and protective covers. PC can be easily molded and post-processed for enhanced aesthetics and functionality. Its durability and versatility make it a preferred choice for demanding engineering applications.
|
 |
| PA
PA (Polyamide), commonly known as Nylon, is a strong and durable engineering thermoplastic with excellent mechanical strength, wear resistance, and chemical stability. It offers high impact resistance, good thermal performance, and low friction, making it ideal for automotive components, industrial gears, bearings, and consumer goods. PA is available in various grades (PA6, PA66, PA12) and can be reinforced with glass fiber for enhanced strength. Its versatility and reliability make it a preferred material for demanding applications.
|
 |
| POM
POM (Polyoxymethylene), also known as Acetal or Delrin, is a high-performance engineering thermoplastic known for its excellent mechanical strength, wear resistance, and low friction. It offers high dimensional stability, chemical resistance, and durability, making it ideal for precision gears, automotive components, bearings, and industrial applications. POM is widely used where high stiffness and low moisture absorption are required. Its self-lubricating properties make it a top choice for moving parts.
|
 |
| PET
PET (Polyethylene Terephthalate) is a strong and lightweight thermoplastic known for its excellent mechanical properties, chemical resistance, and dimensional stability. It offers high stiffness, low moisture absorption, and good heat resistance, making it ideal for food packaging, automotive components, electrical insulators, and industrial applications. PET can be reinforced with glass fiber for enhanced strength and wear resistance. Its durability, recyclability, and versatility make it a widely used material in injection molding.
|
 |
| PEEK
PEEK (Polyether Ether Ketone) is a high-performance thermoplastic known for its exceptional mechanical strength, high-temperature resistance, and chemical stability. It offers excellent wear resistance, low friction, and outstanding dimensional stability, making it ideal for aerospace, medical, automotive, and industrial applications. PEEK is biocompatible, highly resistant to harsh environments, and can replace metals in demanding conditions. Its superior properties make it a preferred choice for precision-engineered components requiring durability and reliability.
|
 |
| PPS
PPS (Polyphenylene Sulfide) is a high-performance thermoplastic known for its exceptional heat resistance, chemical stability, and mechanical strength. It is ideal for injection molding applications in automotive, electronics, and industrial sectors requiring high-temperature and chemical resistance. PPS offers excellent dimensional stability, and low moisture absorption, and can be reinforced with glass or carbon fibers for enhanced strength. It supports precision molding and maintains performance in extreme environments.
|
 |
| LCP
LCP (Liquid Crystal Polymer) is a high-performance thermoplastic known for its exceptional heat resistance, chemical stability, and dimensional precision. It is ideal for injection molding applications in electronics, automotive, and aerospace industries, where ultra-thin walls and intricate details are required. LCP offers excellent mechanical strength, low moisture absorption, and inherent flame retardancy, making it suitable for high-temperature and high-frequency environments. It supports complex geometries with superior moldability and minimal warping.
|
 |
| TPE
TPE (Thermoplastic Elastomer) is a flexible and durable material widely used in injection molding. Combining the elasticity of rubber with the processability of plastics, TPE is ideal for automotive, consumer goods, and medical applications. It offers excellent impact resistance, weatherability, and a soft-touch feel, making it perfect for grips, seals, and over-molding. TPE can be customized for varying hardness levels and enhanced UV or chemical resistance, ensuring versatility in design and performance.
|
 |
| TPU
TPU (Thermoplastic Polyurethane) is a highly durable and flexible material widely used in injection molding. Known for its excellent abrasion resistance, elasticity, and chemical stability, TPU is ideal for automotive, consumer electronics, and industrial applications. It provides superior impact strength, weather resistance, and a soft-touch feel, making it perfect for grips, protective casings, and seals. TPU can be customized for varying hardness levels and enhanced UV or oil resistance, ensuring versatility in demanding environments.
|
 |
Plastic Injection Molding Finishing Options
| Name | Description |
|---|---|

MT/VDI Texture |
Standardized mold etching techniques create surface textures to enhance grip and visual appeal. |
|
Bead Blasting |
Spraying fine particles onto the surface for a matte or uniform roughness, reducing gloss. |

High Gloss Polishing |
Mechanical polishing to achieve a smooth, high-gloss finish, often used for transparent parts like PC light covers. |

Deburring |
Removing sharp edges or burrs through manual, chemical, or ultrasonic methods to improve precision and feel. |

CNC Post-Machining |
Enhancing dimensional accuracy through CNC machining, ideal for high-precision components. |

Painting |
Available in multiple colors and finishes (matte/glossy), enhances appearance and weather resistance. |
| UV Coating | Adds a UV-resistant protective layer to prevent fading and improve wear resistance. |
| Powder Coating | Provides a durable, corrosion-resistant surface for enhanced longevity. |
| Silk Screen Printing | Cost-effective method for logos, text, and designs with strong adhesion. |
| Pad Printing | Suitable for printing on irregular surfaces, commonly used for electronic device casings. |
| Laser Engraving | Permanent marking with high precision, resistant to wear, ideal for branding and high-end products. |
| Electroplating | Common for ABS and PC+ABS materials, adds a metallic finish with improved wear resistance and conductivity. |
| Vacuum Metallization | Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) creates metallic coatings, such as chrome or reflective finishes. |
| Anti-Fingerprint Coating | Reduces fingerprint smudges on high-gloss surfaces. |
| Soft-Touch Coating | Provides a rubber-like texture for a premium feel, commonly used in consumer electronics. |
| Chemical-Resistant Coating | Enhances resistance to acids, alkalis, and solvents, suitable for medical and lab equipment. |
Plastic Injection Molding Manufacturer FAQ
Plastic Injection Molding Service FAQ Guide
In the following guide, you will know everything about Plastic Injection Molding.
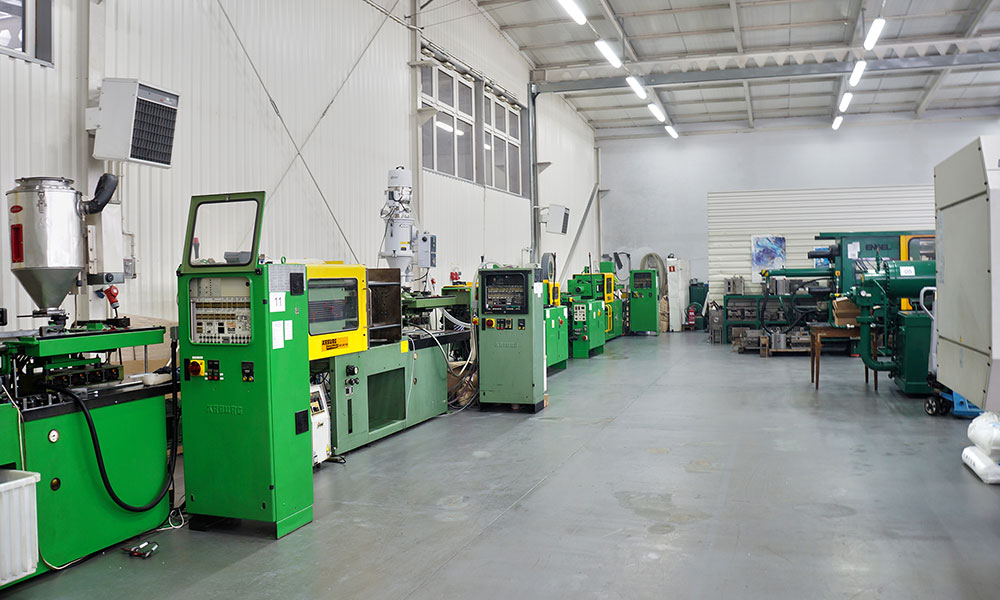
Holly is a professional plastic injection molding supplier. We have more than 40 injection molding machines, the injection volume ranges from 50 tons to 2800 tons, and the maximum injection volume of the product exceeds 10 kg. I hope you can get the plastic injection molding you want to know from this guide.
1. What is plastic injection molding?
Plastic injection molding is a method of injection molding. The advantages of plastic injection molding are fast production speed, high efficiency, automatic operation, product types, from simple to complex shapes, sizes can be large or small, product sizes are accurate, products are easily updated, and shapes are complex. Injection molding is suitable for molding and processing fields such as mass production and products with complex shapes.
2. How many steps are there in injection molding?
Six steps can be roughly divided into the plastic injection molding process: Clamping, injection molding, holding pressure, cooling, opening the mold, and taking out the finished product.
3. What temperature should be paid attention to when plastic injection molding?
During the injection molding process, pay attention to the following three temperatures: cylinder temperature, nozzle temperature, and mold temperature. The first two temperatures mainly affect the plasticization and flow of the plastic, and the latter two temperatures mainly affect the flow and cooling of the plastic.
1) Cylinder temperature
Each type of plastic has a different flow temperature. Due to the different sources or grades of the same plastic, the corresponding average molecular weight and molecular weight distribution are also different, which leads to differences in flow temperature and decomposition temperature. As the plasticizing process is different on the machine, the cylinder temperature is also different.
2) Nozzle temperature
Normally, the nozzle temperature is slightly lower than the maximum temperature of the barrel. This is to prevent “salivation” from possibly occurring in straight-through nozzles. As a result, the nozzle temperature should not be too low, otherwise, the melt will solidify prematurely and block the nozzle, or the injected material will solidify prematurely and cause the product to behave inconsistently.
3) Mold temperature
The temperature of the mold has a significant impact on the product’s internal function and appearance. The mold temperature determines the crystallinity of the plastic, the size and structure of the product, performance requirements and other process conditions (such as melt temperature, injection speed, injection pressure, molding cycle, etc.).
4. What kind of pressure should be controlled during the plastic injection molding process?
Backpressure and injection pressure are both factors into the plastic injection molding process, affecting the plasticization process and product quality.
1) Backpressure
When using a screw grouting machine, the pressure at the top of the screw when the screw rotates and retreats is called backpressure. The size of this pressure can be adjusted by the relief valve in the hydraulic system. In the injection molding process, the size of the plasticizing pressure needs to vary with the screw design, product quality requirements, and plastic types. If these conditions are the same as the screw speed, by increasing the plasticizing pressure, the temperature of the melt will be higher, at the same time, it will reduce the plasticizing efficiency, increase backflow and leakage, and increase the driving power.
2) Injection pressure
In the current production, the injection pressure of almost all injection molding machines is based on the pressure exerted on the plastic by the plunger or the top of the screw. The injection pressure in injection molding is to overcome the flow resistance of the plastic from the cylinder to the cavity and to give the molten material a speed to fill the mold to make the molten material dense.
5. What is the cycle time of plastic injection molding?
The time required to complete an injection molding process is called cycle time. Cycle time directly affects product output and equipment utilization. Therefore, in the production process, under the premise of ensuring quality, the relevant time in the cycle time should be shortened as much as possible. In the entire cycle time, injection time and cooling time are the most important points, because they have a decisive influence on product quality.
The holding time in the injection time is the pressure time of the plastic in the cavity, which accounts for a large proportion of the entire injection time, the average process takes about 20 to 120 seconds (extra-thick parts may require 5-10 minutes). The holding time will only affect the accuracy of the product size before the melt freezes at the gate. The temperature of the mold and the thickness of the product determine the cooling time. The cooling time cannot be too long, because too long cooling time will not only reduce production efficiency, but also make it difficult to demold complex parts, and even produce demolding stress during forced demolding.
6. What is the injection time of plastic injection molding?
For plastic injection molding, the injection time refers to the time required for the plastic melt to fill the cavity, excluding the time for mold opening and closing. Although the injection time is short and has a small impact on the molding cycle, the adjustment of the injection time has a great impact on the pressure control of the gate, runner and cavity. Reasonable injection time is conducive to the ideal filling of the melt, and it is of great significance to improve the surface quality of parts and reduce dimensional tolerances.
The injection time is much lower than the cooling time, about 1/10 ~ 1/15 of the cooling time. This rule can be used as the basis for predicting the total time of plastic injection molding. In the mold flow analysis, only when the melt is completely driven by the screw rotation to fill the cavity, the injection time in the analysis result is equal to the injection time set in the process conditions. If the pressure holding switch of the screw occurs before the cavity is full, the analysis result will be greater than the setting of the process conditions.
7. How do injection molded parts usually deform?
After the plastic part is formed, there will be some defects, which will affect the assembly efficiency or the performance of the overall product. There is a certain difference from the predetermined quality standard (inspection standard), which cannot meet the company’s quality requirements. The following are some common defects of injection molded parts: chromatic aberration, short shot, warpage/deformation, weld marks, burrs, flashes, burn marks, dents, bubbling, ink shots, etc.
8. What is the effect of causing defects in injection molded parts?
In the plastic injection molding process, factors such as mold design, mold manufacturing, raw material characteristics and resin pretreatment methods, molding process, injection molding machine parameters, processing environmental conditions, product cooling time, post-processing technology and other factors affect the quality of injection molded products.
9. What is the holding pressure of plastic injection molding?
At the end of the plastic injection molding process, the screw stops rotating and just moves forward. At this time, plastic injection molding enters the pressure holding stage. In the process of holding pressure, the nozzle of the injection molding machine continuously conveys to the cavity to fill the volume vacated by the contraction of the part. If the pressure is not maintained after the cavity is filled, the parts will shrink by about 25%, especially the ribs will shrink due to excessive shrinkage. Generally, the holding pressure is about 85% of the maximum filling pressure, of course, it should be determined according to the actual situation.
10. What is the injection temperature of plastic injection molding?
In the plastic injection molding process, the injection temperature is an important factor affecting the injection pressure. The barrel of the injection molding machine has 5-6 heating sections, and each raw material has a corresponding processing temperature (for the injection temperature, we can refer to the raw material datasheet). The injection temperature must be within the specified range. If the temperature is too low, the melt plasticization effect will be poor, which will affect the quality of plastic injection molded parts and increase the difficulty of the process; Raw materials decompose easily at too high a temperature. In the actual plastic injection molding process, the injection temperature is always higher than the cylinder temperature, and the higher value is related to the injection rate and the properties of the material, up to 30°C.
11: What is the difference between injection pressure and holding pressure for plastic injection molding?
The function of the injection pressure is to overcome the flow resistance of the melt from the cylinder to the cavity so that the melt enters the cavity with a certain filling rate.
The pressure keeping is to compress the melt in the cavity to make the plastic adhere tightly to the mold wall to obtain a precise shape and to melt the plastic that enters the same part of the cavity at different times and in different directions into a whole.
In the plastic injection molding process, the holding pressure is sometimes equal to the injection pressure, sometimes lower or higher. High pressure can obtain products with higher density, smaller size shrinkage, and better mechanical properties. However, after demolding, the internal residual stress of the product is relatively large, and the pressured product will have a greater rebound after the pressure is released, which may cause it to be stuck in the cavity and cause difficulty in demolding, so the pressure should be appropriate.
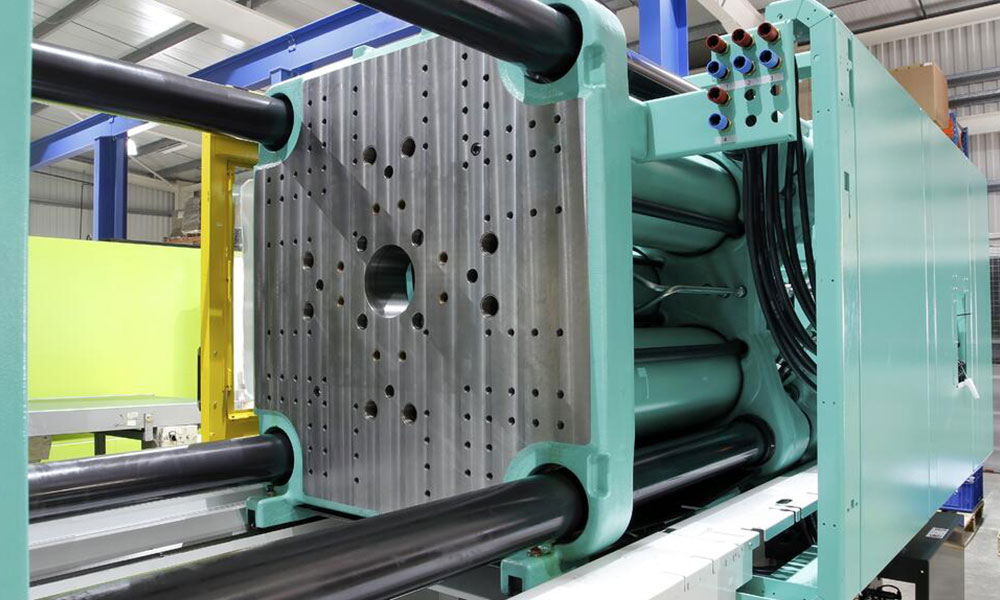
12. What is a plastic injection molding machine?
Plastic injection molding machines are used to make various plastic products using plastic molded molds. The working principle of a plastic injection molding machine is similar to that of a syringe used for injection. It uses the thrust of a screw or plunger to inject the plasticized plastic in a molten state (ie, a viscous state) into a closed mold cavity. It is the process of obtaining products after curing and molding.
13. How many kinds of plastic injection molding machines are there?
Generally speaking, there are three types of plastic injection molding machines according to the external structure. They are vertical injection molding machine, horizontal injection molding machine and angle injection molding machine. Among them, the horizontal injection molding machine is the most commonly used one.
14. What are the advantages of a horizontal injection molding machine?
The horizontal injection molding machine is small in size and easy to operate and maintain. Moreover, the centre of gravity of the machine is low, and the installation is relatively stable. The product falls automatically after being ejected under the action of gravity. The operation is simple and convenient, and fully automatic operation is realized. Therefore, increasing production is the best solution.
15. When should I choose a vertical injection molding machine?
The vertical injection molding machine occupies a small area and is easy to place plug-ins. In addition, the plastic injection mold is easy to load and unload. The material falling from the hopper can be plasticized more uniformly. A vertical plastic injection molding machine is suitable for small plastic injection molding machine. Generally speaking, vertical injection molding machines below 60 grams are more commonly used. Large and medium-sized machines are not suitable and are rarely used.
16. How to buy an injection molding machine?
Injection molding machines are commonly used machines for plastic processing. For operators who use and purchase injection molding machines, they must first understand the performance of a good injection molding machine and the aspects that need to be evaluated. Let’s take a look at some tips for buying injection molding machines.
- The technical parameters of the injection molding machine. We should choose the appropriate plastic molding machine according to the material, shape, structure, application field and specific occasions of the injection molded products. In addition, the structure, quality, precision, number of cavities, runner type, and product structure, shape, and size of the mold should also be considered. In addition, we must also consider production capacity and automation levels.
- Choose suppliers who provide high-quality after-sales service.
- Pay attention to the machine model.
- Easy operation is important for the machine.
- The machine has a high degree of automation, complete functions and high production efficiency.
- Energy conservation and environmental protection should also be considered when purchasing injection molding machines.
17. How many injection molding machines does Holly have?
The size of the injection molding machine ranges from 50 tons to 2,800 tons. There are 23 units in the ordinary injection workshop and 22 units in the cleanroom injection workshop. In addition, we have 6 double-needle injection molding (double injection molding) machines. In addition, the size of our largest double-rod injection molding machine is 1,300 tons.
18. Why is the injection molded part deformed?
For the deformation of plastic injection parts, there are the following two situations. The first case is that deformation occurs during or immediately after demolding. In one situation, the deformation occurs during curing or after demolding as a result of poor deformation conditions established during the plastic injection molding process. In the other situation, the deformation occurs due to poor injection pressure conditions set during the process.
19. How to improve the deformation of injection molded parts?
Here are some tips to improve the deformation of plastic injection molded parts.
A. Plastic materials
- Replace high-strength/fiber-reinforced plastics.
- Replace the high-release efficiency additive-grade material section
B. Mould
- Check the stability/calibration rate of the cooling pipe
- Increase cooling pipe
- Improve the flatness of the lower die
- Increase the angle of mold release
- Check/add mold exhaust pipe
- Optimize the injection system
- Improve mold strength
- Increase the formed ribs
C) Injection molding machine parameters
- Reduce stress
- Reduce the holding time
- Optimize the transmission pressure point
- Reduce mold temperature
- Optimize injection speed
- Increase cooling time
20. How to improve the flash of injection molded parts?
Usually, we use the following points to improve the flash of plastic injection molded parts.
A) Plastic
- Replace materials with low flow rates.
B) Mould
- Check the damage of the mold
- Optimize the ratio of mold wall thickness to thinness difference
- Change the gate position
- Check/enhance mold structure and strength
C. Injection molding machine parameters
- Grading and optimization of injection pressure
- Reduce injection pressure
- Optimize the holding pressure conversion position
- Reduce holding pressure
- Reduce the injection speed
- Reduce pressure holding time
- Reduce injection temperature
- Reduce mold temperature
- Increase clamping pressure
- Replace the model with a larger clamping force
- 1. What is plastic injection molding?
- 2. How many steps are there in injection molding?
- 3. What temperature should be paid attention to when plastic injection molding?
- 4. What kind of pressure should be controlled during the plastic injection molding process?
- 5. What is the cycle time of plastic injection molding?
- 6. What is the injection time of plastic injection molding?
- 7. How do injection molded parts usually deform?
- 8. What is the effect of causing defects in injection molded parts?
- 9. What is the holding pressure of plastic injection molding?
- 10. What is the injection temperature of plastic injection molding?
- 11: What is the difference between injection pressure and holding pressure for plastic injection molding?
- 12. What is a plastic injection molding machine?
- 13. How many kinds of plastic injection molding machines are there?
- 14. What are the advantages of a horizontal injection molding machine?
- 15. When should I choose a vertical injection molding machine?
- 16. How to buy an injection molding machine?
- 17. How many injection molding machines does Holly have?
- 18. Why is the injection molded part deformed?
- 19. How to improve the deformation of injection molded parts?
- 20. How to improve the flash of injection molded parts?