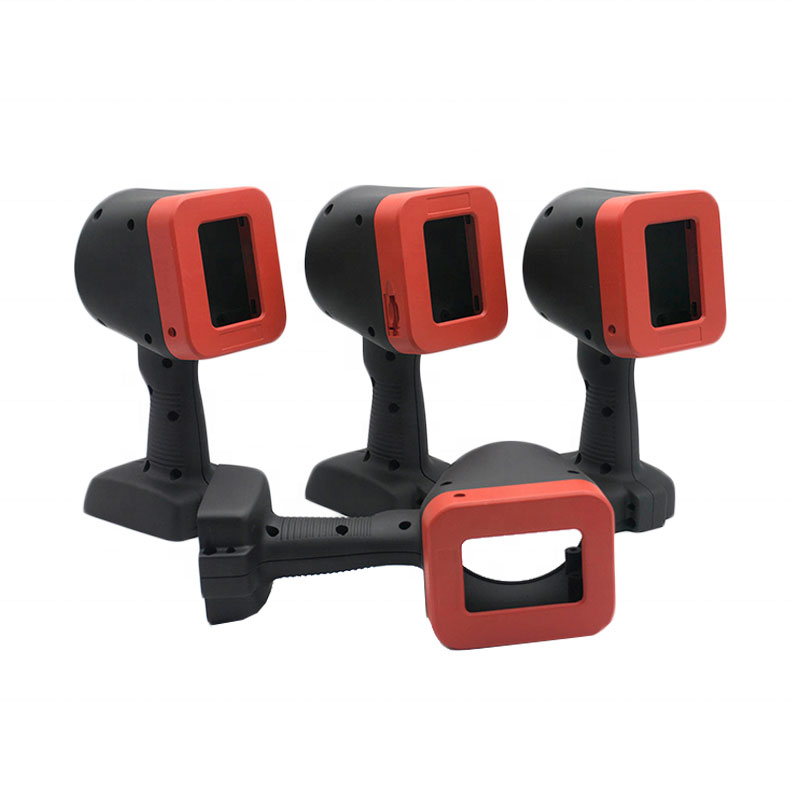
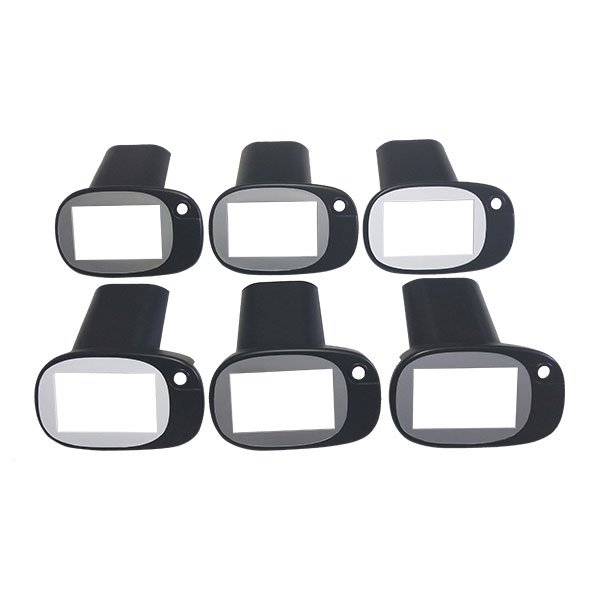
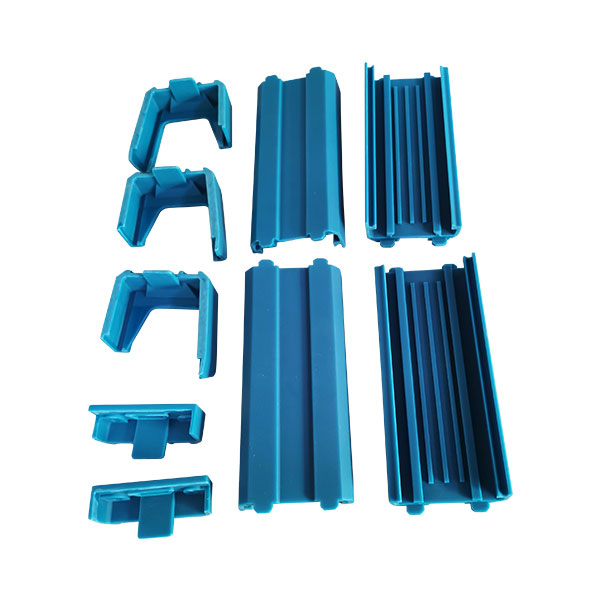
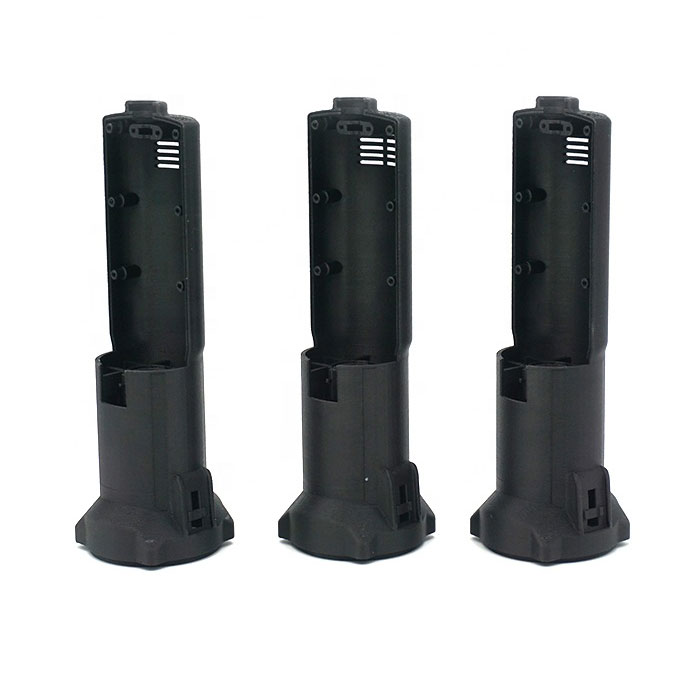
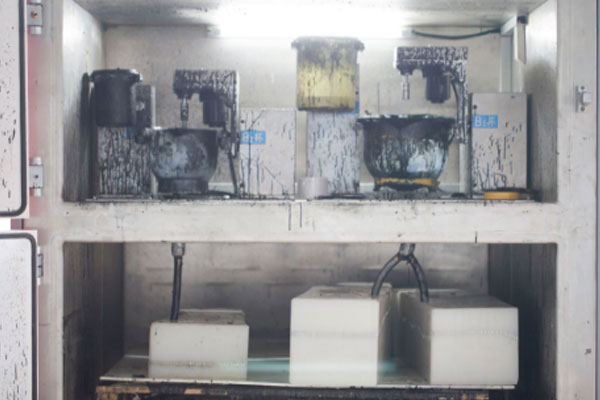
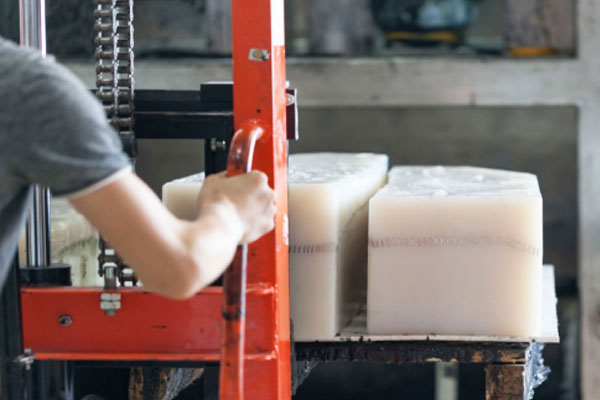
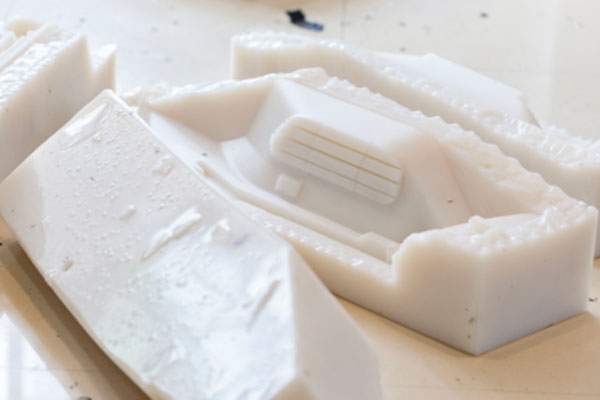
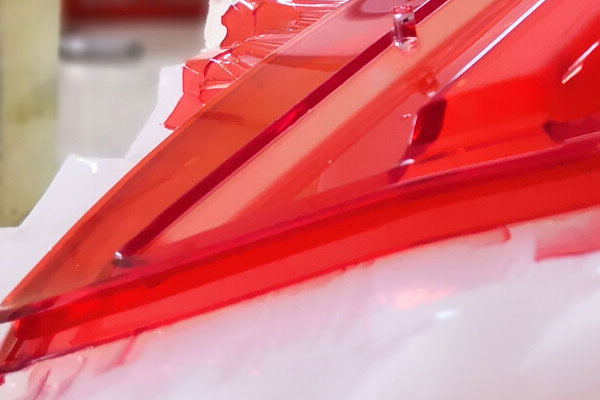
Vacuum Casting Company from China
Holly specializes in precision vacuum casting, providing rapid prototyping and small-batch production solutions for industries such as automotive, electronics, medical, and industrial equipment. Our advanced process ensures high-quality parts with fine details and smooth surface finishes.
We start by creating a master model using CNC machining or 3D printing, which can be completed in as fast as one day. After tolerance checks and approval, our team produces a high-precision silicone mold within 3-4 days. The vacuum casting process takes another 2-3 days, allowing us to deliver your final parts within 7-14 days.
Holly offers a wide range of materials, from rigid plastics to flexible rubber-like resins, and can produce parts ranging from small components to 2-meter-long automotive bumpers. We use only the highest quality resins from top international brands, ensuring excellent durability and performance.
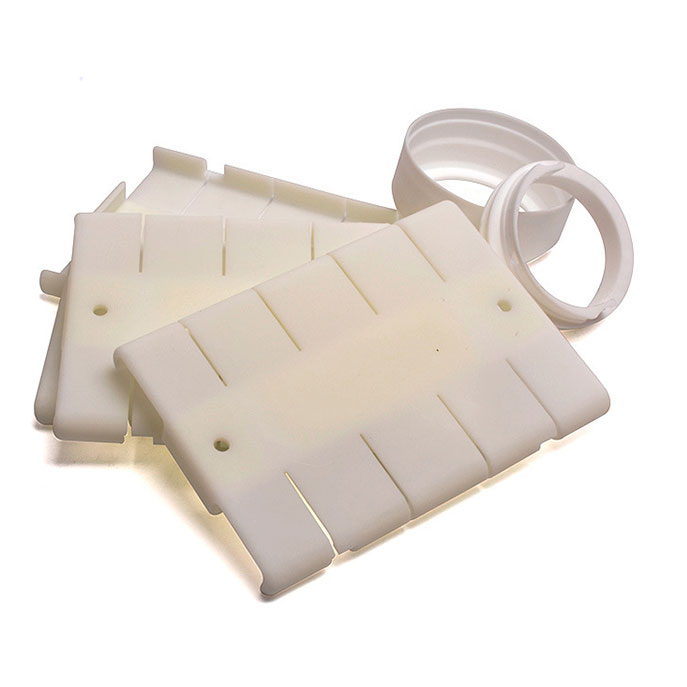
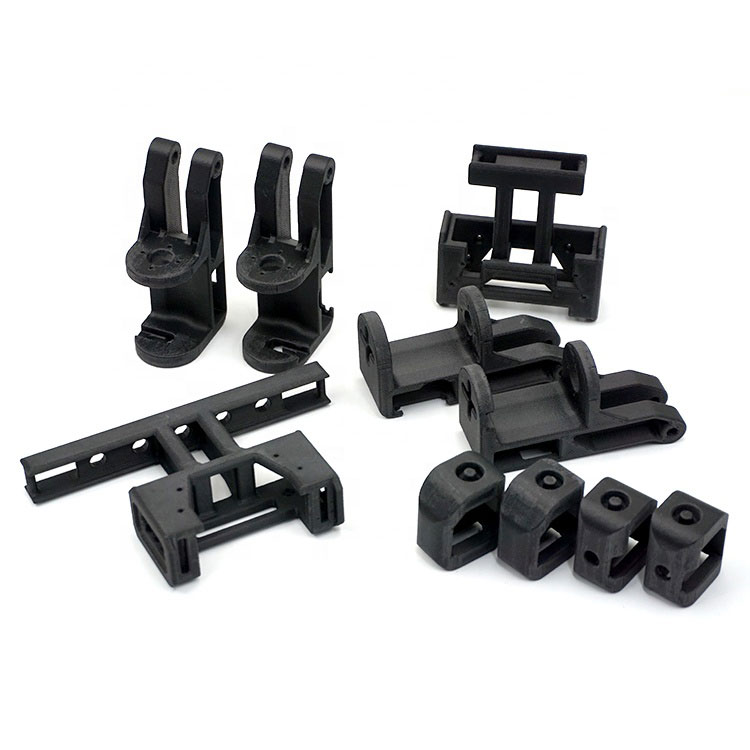
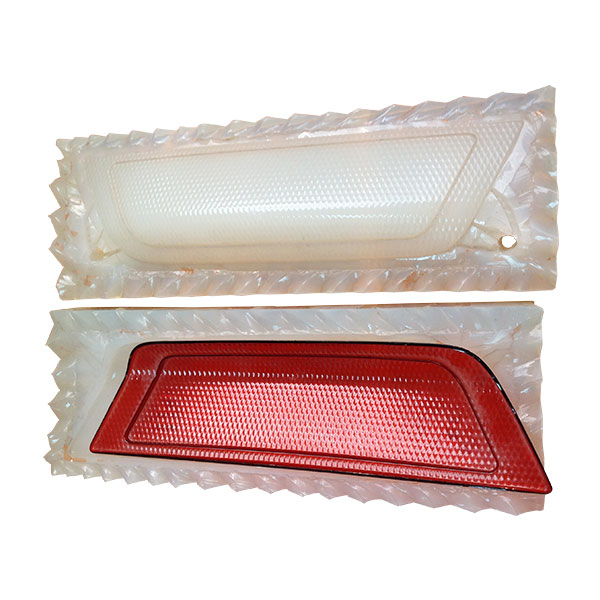
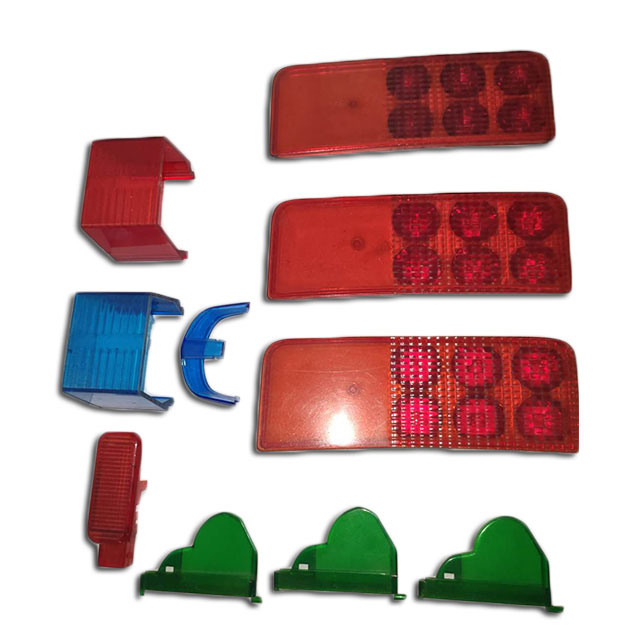
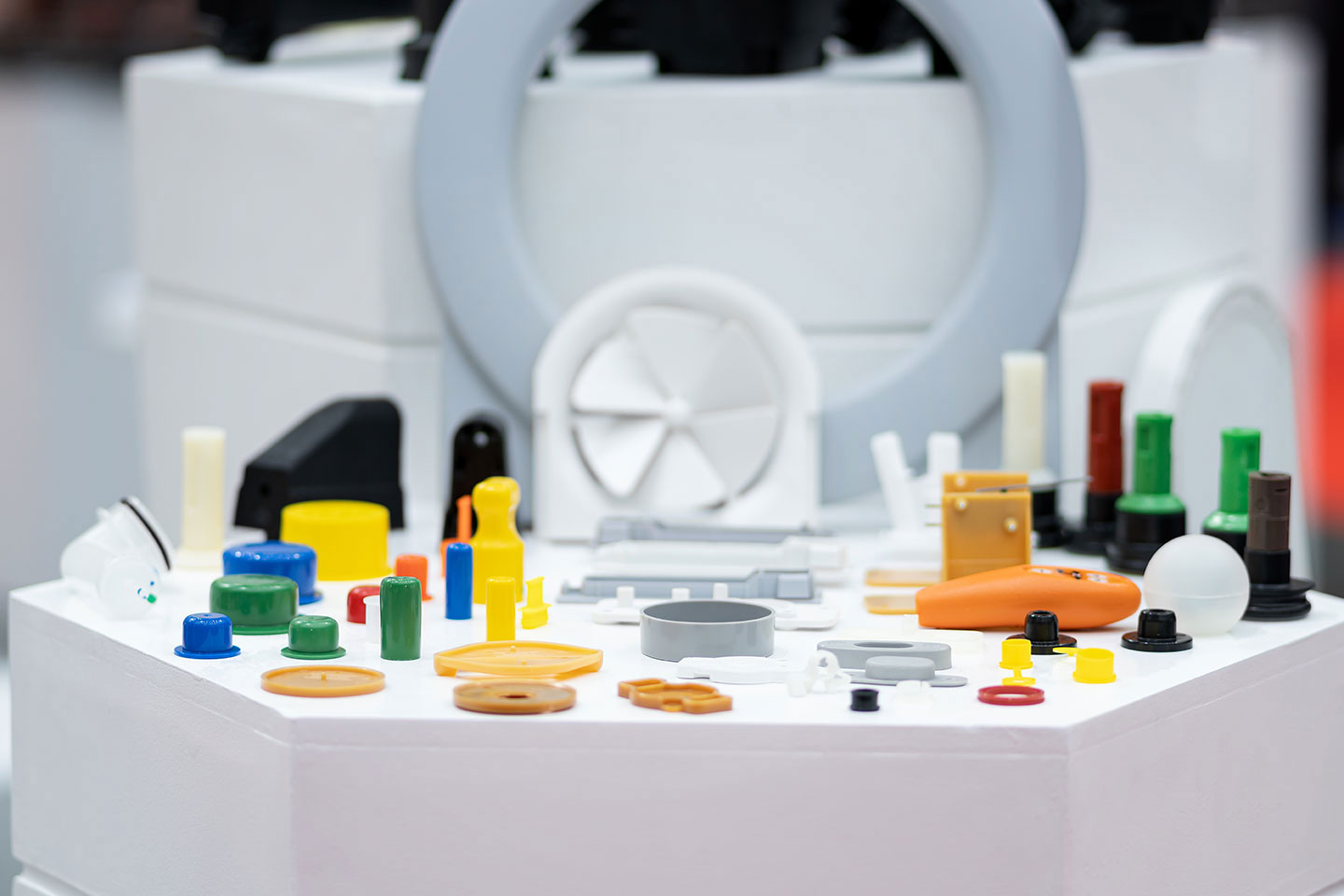
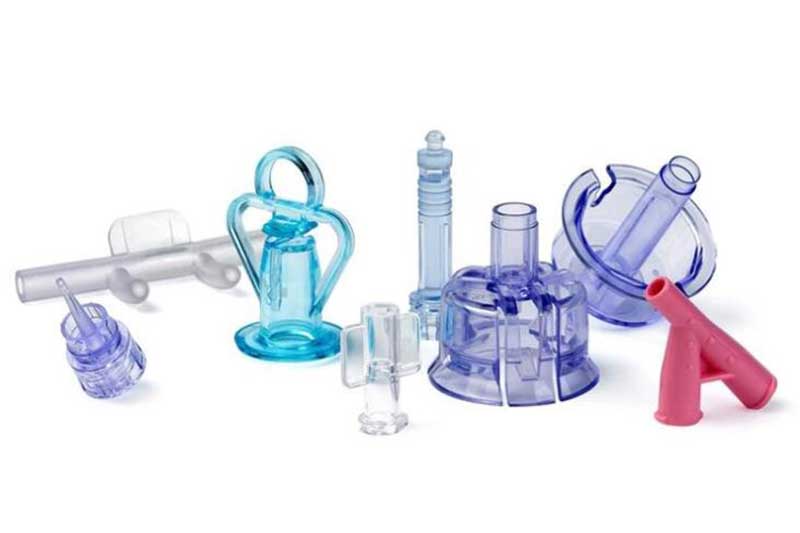
Explore Vacuum Casting Parts We Manufactured
Holly specializes in Vacuum Casting solutions, delivering high-quality prototypes and low-volume production for various industries. Our product categories include automotive parts, medical device housings, consumer electronics prototypes, industrial enclosures, and custom precision components. With superior surface finish, high accuracy, and material versatility, our vacuum-cast products meet stringent design and performance requirements, ensuring cost-effective and rapid production for your business needs.
Vacuum Casting Capabilities
Vacuum Casting Material Available
| PU-like ABS
PU-like ABS is a high-performance polyurethane resin designed to mimic the mechanical properties of ABS plastic. It offers excellent strength, impact resistance, and surface quality, making it ideal for prototyping and small-batch production in automotive, consumer electronics, and industrial applications. This material supports painting and plating, allowing for both functional and aesthetic parts. PU-like ABS is cost-effective, easy to process, and provides a fast turnaround for vacuum casting projects.
|
 |
| PU-like PC
PU-like PC is a high-performance polyurethane resin that replicates the properties of polycarbonate (PC). It offers exceptional transparency, impact resistance, and heat stability, making it ideal for automotive lighting, consumer electronics, and industrial applications. This material supports various surface treatments, including tinting and coating, for both functional and aesthetic components. PU-like PC provides a cost-effective solution for rapid prototyping and small-batch production, ensuring high optical clarity and durability.
|
 |
| PU-like PMMA
PU-like PMMA is a high-transparency polyurethane resin designed to simulate the optical clarity and rigidity of acrylic (PMMA). It offers excellent light transmission, scratch resistance, and surface quality, making it ideal for automotive lenses, consumer electronics, and display components. This material supports tinting and polishing for enhanced aesthetics and functionality. PU-like PMMA provides a cost-effective solution for rapid prototyping and small-batch production, ensuring high optical performance and durability.
|
 |
| PU-like POM
PU-like POM is a durable polyurethane resin engineered to mimic the strength, rigidity, and low friction properties of polyoxymethylene (POM). It offers excellent wear resistance, dimensional stability, and mechanical performance, making it ideal for gears, bearings, and precision industrial components. This material provides a cost-effective solution for prototyping and small-batch production while maintaining the toughness and self-lubricating properties of traditional POM.
|
 |
| PU-like TPU
PU-like TPU is a flexible polyurethane resin designed to replicate the elasticity, toughness, and abrasion resistance of thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU). It offers excellent durability, impact resistance, and flexibility, making it ideal for seals, gaskets, grips, and wearable components. This material provides a cost-effective solution for prototyping and small-batch production while maintaining the soft-touch feel and resilience of traditional TPU.
|
 |
| PU-like Rubber
PU-like Rubber is a flexible polyurethane resin engineered to replicate the elasticity, durability, and non-slip properties of traditional rubber. It offers excellent impact absorption, tear resistance, and flexibility, making it ideal for seals, gaskets, handles, and vibration-dampening components. This material provides a cost-effective solution for prototyping and small-batch production while maintaining the soft-touch feel and resilience of conventional rubber.
|
 |
| PU-like Silicone
PU-like Silicone is a flexible polyurethane resin designed to replicate the softness, elasticity, and heat resistance of traditional silicone. It offers excellent tear strength, chemical resistance, and biocompatibility, making it ideal for medical devices, seals, gaskets, and soft-touch components. This material provides a cost-effective solution for prototyping and small-batch production while maintaining the durability and flexibility of conventional silicone.
|
 |
| High-Temp PU
High-Temp PU is a polyurethane resin engineered for superior heat resistance, maintaining structural integrity at temperatures up to 150°C. It offers excellent mechanical strength, impact resistance, and dimensional stability, making it ideal for automotive, aerospace, and industrial applications exposed to high temperatures. This material provides a cost-effective solution for prototyping and small-batch production while ensuring durability under thermal stress.
|
 |
| Flame-Retardant PU
Flame-Retardant PU is a polyurethane resin designed for enhanced fire resistance, meeting UL 94 V-0 standards for flame retardancy. It offers excellent mechanical strength, impact resistance, and heat stability, making it ideal for electrical housings, automotive components, and industrial applications requiring fire safety compliance. This material provides a cost-effective solution for prototyping and small-batch production while ensuring durability and safety in high-risk environments.
|
 |
| Transparent PU (PC-like)
Transparent PU (PC-like) is a high-clarity polyurethane resin engineered to replicate the optical transparency, impact resistance, and heat stability of polycarbonate (PC). It offers excellent light transmission, durability, and scratch resistance, making it ideal for automotive lenses, electronic displays, and protective covers. This material provides a cost-effective solution for prototyping and small-batch production while maintaining high optical performance and mechanical strength.
|
 |
| Transparent PU (PMMA-like)
Transparent PU (PMMA-like) is a high-clarity polyurethane resin designed to mimic the optical transparency, rigidity, and light transmission of acrylic (PMMA). It offers excellent surface quality, scratch resistance, and UV stability, making it ideal for lighting covers, display panels, and aesthetic components. This material provides a cost-effective solution for prototyping and small-batch production while ensuring superior optical performance and durability.
|
 |
| Chemical-Resistant PU
Chemical-Resistant PU is a polyurethane resin engineered for superior resistance to acids, alkalis, solvents, and oils. It offers excellent mechanical strength, impact resistance, and dimensional stability, making it ideal for chemical processing equipment, industrial seals, and protective housings. This material provides a cost-effective solution for prototyping and small-batch production while ensuring durability in harsh chemical environments.
|
 |
| UV-Resistant PU
UV-Resistant PU is a polyurethane resin formulated to withstand prolonged UV exposure without yellowing, cracking, or degrading. It offers excellent mechanical strength, impact resistance, and weatherability, making it ideal for outdoor applications, automotive components, and consumer electronics. This material provides a cost-effective solution for prototyping and small-batch production while ensuring long-term durability in sun-exposed environments.
|
 |
Vacuum Casting Finishing Options
| Name | Feature | Material | Can be applied with |
|---|---|---|---|

Painting |
Provides different colors, gloss levels (matte, semi-gloss, or high-gloss), and texture effects. | PU-like ABS, PU-like PC, PU-like POM, High-Temp PU, and Flame-Retardant PU. | Consumer electronics, automotive parts, industrial equipment housings. |
|
Polishing |
Removes mold texture to enhance smoothness and transparency, particularly for clear materials. | Transparent PU (PC-like), Transparent PU (PMMA-like). | Transparent housings, automotive light covers, optical components. |

Sandblasting |
Uses fine particles to create a uniform matte or frosted texture, reducing fingerprints and glare. | PU-like ABS, PU-like PC, PU-like POM, PU-like TPU, PU-like Rubber. | Consumer electronics casings, handles, and medical devices. |

Texturing |
Adds surface texture via chemical etching or mold treatment to improve grip or aesthetics. | PU-like ABS, PU-like TPU, PU-like Rubber. | Handles, control panels, buttons. |

Tinting |
Applies color to transparent materials while maintaining light transmission. | Transparent PU (PC-like), Transparent PU (PMMA-like). | Automotive light covers, electronic screens, decorative transparent parts. |

Plating/Metal Coating |
Enhances metallic appearance, wear resistance, or conductivity. | PU-like ABS, PU-like POM (with optional conductive coating). | Automotive trims, electronic device housings, industrial components. |
| UV Coating | Increases wear resistance, UV protection, and gloss or anti-fingerprint properties. | Transparent PU (PC-like), Transparent PU (PMMA-like), UV-Resistant PU. | Outdoor equipment, automotive interiors, consumer electronics. |
| Screen Printing & Laser Etching | Adds logos, text, or patterns to the surface.
Removes surface coatings to create high-contrast markings, such as button labels. |
PU-like ABS, PU-like PC, PU-like POM. | Electronic devices, control panels, automotive dashboards. |
| Hot Stamping | Adds a metallic gloss or other decorative effects to the surface. | PU-like ABS, PU-like PC. | Premium electronic casings, automotive trims. |
Vacuum Casting Services FAQ
Vacuum Casting FAQ Guide
In the following guide, you will know everything about Vacuum Casting Service
If you want to know what is the most economical way to make a prototype? Then you should try vacuum casting. In vacuum casting, you need to have the right and optimal temperature to cure the material. For resin, when the vacuum pressure time is 5 minutes and the mold temperature is 60 degrees Celsius, you need 30 degrees Celsius to minimize shrinkage.
Vacuum casting is the same replication using silicon molds. The use of silicone molds for plastic vacuum casting was developed in a German university in the 1960s. What are the benefits of vacuum casting for your company? Continue reading this article to find out.
1. What is Vacuum Casting?
Vacuum casting is an elastomer casting process that uses a vacuum to suck any liquid material into the mold. When vacuum casting is used, air trapping is a problem with the mold. In addition, this process can be used when there are complex details and cuts on the mold. In addition, if the material used to make the mold is fibre or reinforced steel wire, it is also applicable.
Sometimes, vacuum casting is also called thermoforming, because the process of manufacturing involves rapid prototyping, and the plastic sheet is preheated. These materials are preheated in an automatic vacuum casting machine until they become soft and flexible.
2. Why Choosing Vacuum Casting?
The result of the vacuum casting process is a high-quality product compared to injection molded components. Vacuum casting models are often used for functional testing and marketing purposes. The final product has such a good ending, this technology has attracted a large number of viewers. The finishing method of vacuum casting is unmatched by any other process.
1) The product has high precision and fine details
When you use silicone as a mold and moldy to your product. It ensures that the final product has a great interest in details. The final product looks just like the original product.
Every interest in information is considered and also considered. Even if the original product has the most complex geometry, the final product looks like the original product.
2) High-quality products
The products produced by the vacuum casting process are of high quality. In addition, the use of resin allows you to choose the ideal product for the final product produced.
This enables you to have more flexibility, hardness, and hardness options in your project. Also, considering that the product used plays an important role, this has an excellent effect on the final appearance of the product.
3) Lower Production Costs
It is more cost-effective to use the vacuum casting process to make products. This is because this process uses silicon to make molds and mold. Compared with aluminium or steel, silicone resin has a lower cost and can produce excellent end products.
In addition, this material allows you to make more products from mold and mildew. This makes the process more budget-friendly compared to using 3D printing.
4) Fast Delivery
This method is fast, and it takes less time to complete the completed project. You may need 7 to 10 days to make about 50 operable model parts. This technique is amazing when you make a large number of items. In addition, if you can complete the task before the deadline, that would be great.
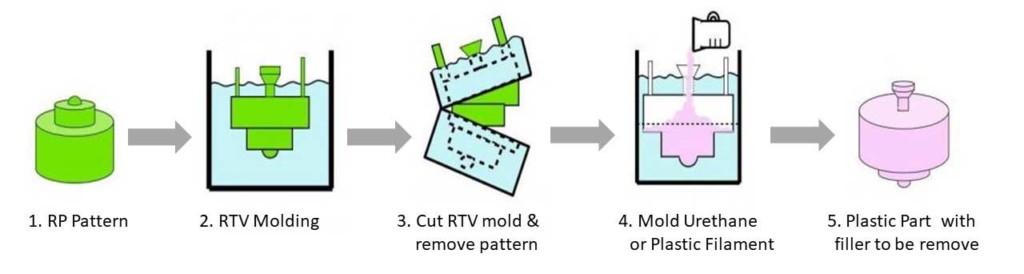
3. How Does Vacuum Casting Work?
Casting of polyurethane must be carried out under vacuum to guarantee the excellent characteristics of mechanical strength and surface finish typical of this technology.
Typically, the master is obtained by 3D printing, possibly using a technique that provides a good surface finish, such as stereolithography, and depending on the properties of the piece to be obtained (mechanical strength, transparency, colour, elasticity, weight, conductivity, flame retardancy, etc.) choose cast polyurethane.
Alternatively, the master can also be achieved by other techniques (CNC, hand modelling), it can also be made from a commercially available detail, an old product or a piece of art. Even casting materials can be of different types: Epoxies, waxes, ceramics and composites can replace polyurethane.
Vacuum casting can be used to assemble different materials, for example, to incorporate bushings, pins, different types of inserts, electronic boards, and also to overmolding two different plastic materials or one plastic and one elastomer. In contrast, compared to mass-production solutions such as injection molding:
- This is convenient if there are very few things to do;
- It allows to manage some back cuts without using inserts;
- Within certain limits, the presence of variable thickness can be accepted without significant deformation of the workpiece.
4. Vacuum Casting Process
The vacuum casting process follows different process stages to manufacture raw materials and complete finished products. Everything takes place in a casting vacuum chamber. Let’s see the step-by-step process of how vacuum casting works:
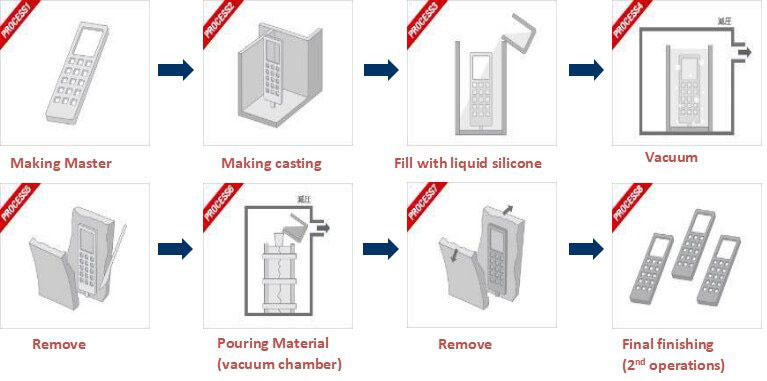
1) Have a high-quality master model
The vacuum casting process requires you to have a high-quality master mold. The high-quality master model can be the industrial component itself. In addition, you can use a model created using stereolithography, which is an example of application prototyping.
You should always make sure that the master model used has the correct size and appearance. This is to ensure that no defects are transferred to the model prototype after the completion of the process.
2) Cure Process
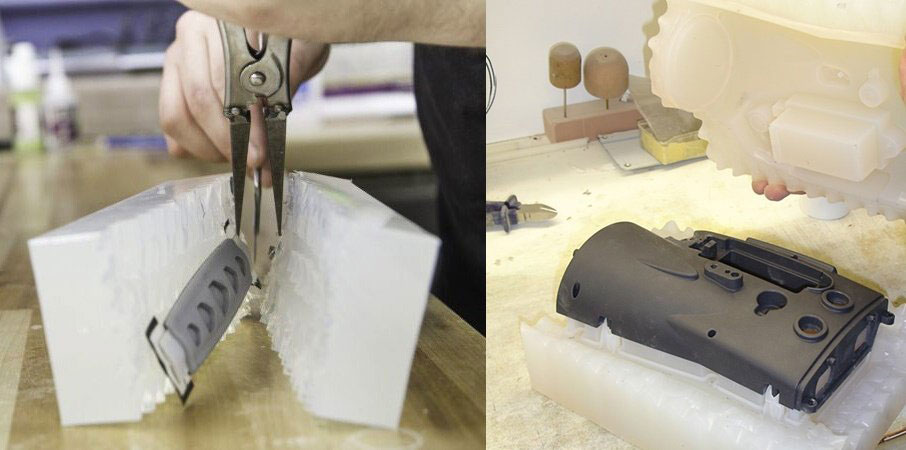
Then, the master model is encapsulated in a two-part silicone rubber mold. The mold is cured at a high temperature to ensure that the two parts stick together. In this way, the mold can be stronger and more durable.
After the mold is cured, it is cut open to expose a hollow space in the centre, which is consistent with the precise dimensions of the main model. After the mold is cut into two sections, it is placed in a vacuum chamber. Then, fill the specified material in the mold to make the product.
3) Filling The Resin
You should fill the mold with the specified material. This resin has the characteristics of industrial material. Resin materials are usually mixed with metal powders or any coloured pigments to achieve aesthetics or specific functional properties.
After filling the mold with resin material, it is placed in a vacuum chamber. Place in a vacuum chamber to ensure that there are no bubbles in the mold. This is to ensure that the final product is not destroyed or damaged.
4) Final Cure Process
The resin is put into the oven for the final curing stage. The mold is cured at a high temperature to ensure that the material is strong and durable. The silicone mold is removed from the mold so that it can be used to make more prototypes.
After the prototype is taken out of the mold, it is painted and decorated. Painting and design are used to ensure that the product has a gorgeous final appearance.
5. Benefits of vacuum casting
Vacuum casting is more economical than 3D printing or injection molding. This allows you to produce more items at a lower cost. Visit this website and learn more about vacuum casting and the use of silicone molds and mold using this extraordinary modern technology.
1) Better than injection molding
Because injection molding is more commonly used than vacuum casting, many organizations may not even consider the vacuum casting process of their parts. However, in some specific cases, silicone-based surgery is more worthwhile and may be of higher quality.
2) Quantity
For a large number of components, it is difficult to see injection molding. Although the set-up price of injection molding is high (even with rapid mold), the equipment cost is very low. This means that when a company needs hundreds or thousands of duplicate parts, the upfront cost of installation can be easily compensated by saving each part.
On the other hand, not every organization needs hundreds or thousands of copies of a component. When fewer parts are required, vacuum casting may be a better choice, as installation costs are greatly reduced.
3) Detail
Since molds are usually made of high-quality metal, shot peening can develop more complete parts compared to vacuum casting. Therefore, for highly complex parts, shot blasting is a better choice.
For less complex parts, especially those that only need to be manufactured in small quantities, vacuum casting can be more effective. This is not a simple and affordable alternative: vacuum casting can use extremely smooth surfaces, which means direct components may look better when vacuum casting is used.
4) Rate and version
Vacuum casting reduces configuration costs and has a good knock-on effect. If the design needs to be modified at any stage in the manufacturing process, changing the vacuum casting mold and mold is much easier and more affordable than redesigning the mold or reusing the mold for injection.
Generally speaking, this means that in the early stages of development, vacuum casting is usually a better choice. In fact, organizations often use vacuum casting to make very early models before creating end-use components or late-stage prototypes using injection molding.
Importantly, producing molds and molds for vacuum casting is much faster than creating molds for pellet casting, which means that vacuum casting is usually more suitable for very small numbers of time-sensitive prototype tasks. (The larger the batch, the faster the injection molding.)
5) Material considerations
Even if all indications indicate vacuum casting, we must remember that some prototypes—especially those that will undergo physical screening—need to be as close as possible to the end-use part. Therefore, if a useful part will eventually use injection molding, it may be beneficial to prototype using the same process, even if the cost is higher.
6. Vacuum Casting Material
We offer 26 carefully selected polyurethanes, similar to rubber, PP, ABS, and PC. These materials provide excellent various properties and the possibility of matching colours and casting transparent components. If you are looking for a specific finish, our skilled vacuum casting post-production team will meet your requirements. Contact us for more detailed information to find the best material for your project.
7. How to Select Material For Vacuum Casting
With the wide application of vacuum casting technology and the advantages it brings, research on it and its materials are particularly important. This article will tell you the types of materials we use in vacuum casting and what exactly these materials simulate. I hope this article will help you gain more knowledge about vacuum casting materials.
1) Factors to consider when choosing materials
When we will see different types of materials for our use, it is important to ensure that they meet certain characteristics or certain factors.
In addition, due to the wide range of materials available, it may be slightly more difficult to find a perfect match for a particular characteristic. This requires research on specific materials to find out which materials are more suitable for a specific character than other materials. This wide availability also ensures that the material must be able to meet any type of demand, no matter how specific it may be.
Vacuum casting materials are expected to have the following characteristics to a certain extent:-
- Surface finish
- Stiffness
- Temperature resistance
- colour
- flexibility
- strength
- Quality appearance
- Transparency or certain levels of translucent properties
- UV stable
The above factors are our basic understanding of the materials used in vacuum casting. Different materials will have different levels of these properties, and we must use them accordingly to adapt to our prototype.
2) A general study of materials and their properties
Now that we know that materials need to follow certain characteristics or characteristics, the next step is to find out which materials have which characteristics. In this section, we will look at the strength of materials and where these strengths can be applied.
Vacuum casting adopts thermoplastic polyurethane material. The important thing is that the materials we use in vacuum casting must accurately show performance similar to elastomer rubber, ABS, etc. This ensures access to a wider range of properties and enables multiple opportunities to be applied and a wide variety of components to be converted.
Vacuum casting materials expect to simulate materials and their special properties as follows:
- High flexibility of rubber.
- As shown by ABS, it has high hardness, strength and transparency.
- High elastic properties of polypropylene and HDPR.
- High rigidity of glass-filled nylon and polyamide.
Resistance to impact and high temperature, as shown by PMMA and polycarbonate.
Flame-retardant and flame-retardant properties of filled ABS
We can cite some examples of materials that successfully simulate some of the properties in the above list and are very useful in vacuum casting.
| Type |
Material |
Simulates |
Properties |
|
Rigid/ Semi-Rigid |
SG95 |
ABS |
Transparency |
|
Specialist Material |
PX330 |
ABS |
Retardance/Fire Resistance |
|
Elastomers |
6130 |
90A Rubber |
High Tear Strength |
|
Specialist Material |
PX5212 |
PC |
UV Stable |
3) Application of vacuum casting materials
As we have seen, the materials used for vacuum casting have a large number of properties. This ensures that they have a wide-ranging impact on the manufacturing industry. Let’s take a look at some of them.
- The automotive industry has used the influence of vacuum casting materials to increase the mass production of automotive parts.
- These products are used in the consumer goods industry to make decorative pieces such as display pieces and wall plaques.
- As vacuum casting technology is used in medical equipment and has made great progress in prosthetics, the medical industry has benefited a lot from vacuum casting technology.
- In addition to the above points, vacuum casting materials are used by engineers in multiple industries, such as telecommunications, aerospace and food production.
8. Application of Vacuum Casting
Vacuum casting is used in the food and beverage sector to make bottles and cans. It is also used in business projects and housing projects.
1) Food and drink
The food and beverage market uses this product to package its final product. Vacuum casting can be used to make plastic bottles and plastic cans. Considering that this process can be used to make props quickly and can be used on a large scale, this process is chosen in most fields.
2) Commercial products
This program is used to make commercial items that can be used for packaging. Most of the items used in this process include sunglasses, mobile phone cases, food and beverage packaging, and pens. This method creates employment opportunities for those who want to risk selling these products.
4) Household products
Some household products use vacuum casting technology. Daily necessities, such as detergents, food processing, and cosmetics are all made using this procedure. If your product comes from a high-quality company, they are likely to use the vacuum casting process to manufacture the product.
9. How much does it cost for vacuum casting
Obviously, it is difficult to give a cost indicator valid for each model, but in general, it can be said that the cost of a mould can vary between 200 and 1000€, although the cost per piece can vary by 10 to 100€, from getting Simple fragments to increasingly complex geometries. Considering that each mold can be printed around 20 times, the single cost including equipment is between 20 – 150 euros. These costs can be reduced if multi-mode molds can be produced or cheaper materials can be cast.
10. When does the silicone molding make sense?
These technical and economical features make silicone molds an ideal solution for different situations:
Small series of products, niche products (tens to hundreds of pieces);
Production of customized products of different sizes that are difficult to manage with injection molds;
For the intermediate development of a project, when all the details have not been defined, but you want to start testing a small series of areas in the final product;
A project of advanced development, when you have a product that is basically market-ready, but you are not able to generate large quantities (because of the cost and time to set up the equipment, because the market is very variable in terms of consumer demand and available components);
Copy and copy objects without CAD models, which can be craft models, works of art, natural objects;
Manufacture of spare parts for non-production products whose market quantities are believed to be incompatible with mass production.
In the latter two cases, the silicone molding solution is usually a cheaper alternative, compared to the reverse engineering process that involves: scanning, data processing, CAD remodelling, which can be very expensive and not always necessary.
11. Conclusion
Holly offers a variety of prototyping processes, from industrial-grade CNC machining to FDM 3D printing. Small rolls of plastic parts, however, are usually used by companies in injection molding-usually using liquefied materials in the process of injecting steel mold and mold, vacuum casting, and more affordable silicone molds for the development of small-batch plastic components.
- 1. What is Vacuum Casting?
- 2. Why Choosing Vacuum Casting?
- 3. How Does Vacuum Casting Work?
- 4. Vacuum Casting Process
- 5. Benefits of vacuum casting
- 6. Vacuum Casting Material
- 7. How to Select Material For Vacuum Casting
- 8. Application of Vacuum Casting
- 9. How much does it cost for vacuum casting
- 10. When does the silicone molding make sense?
- 11. Conclusion