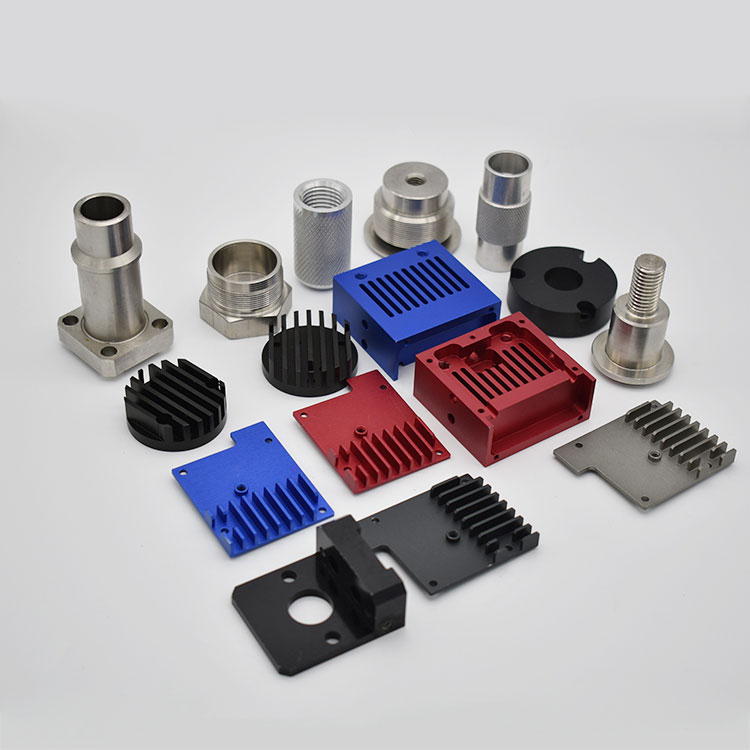
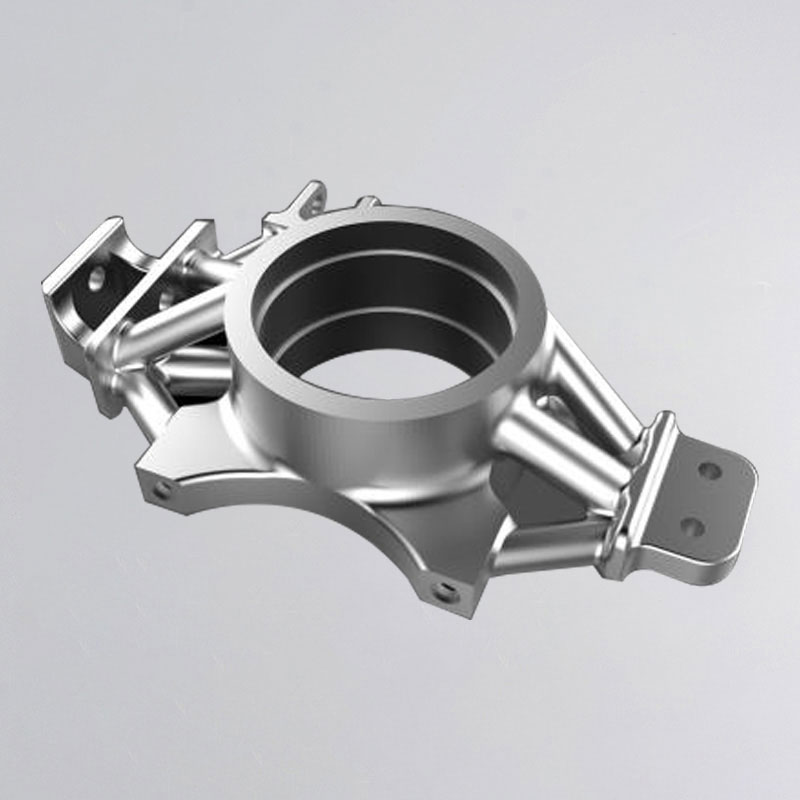
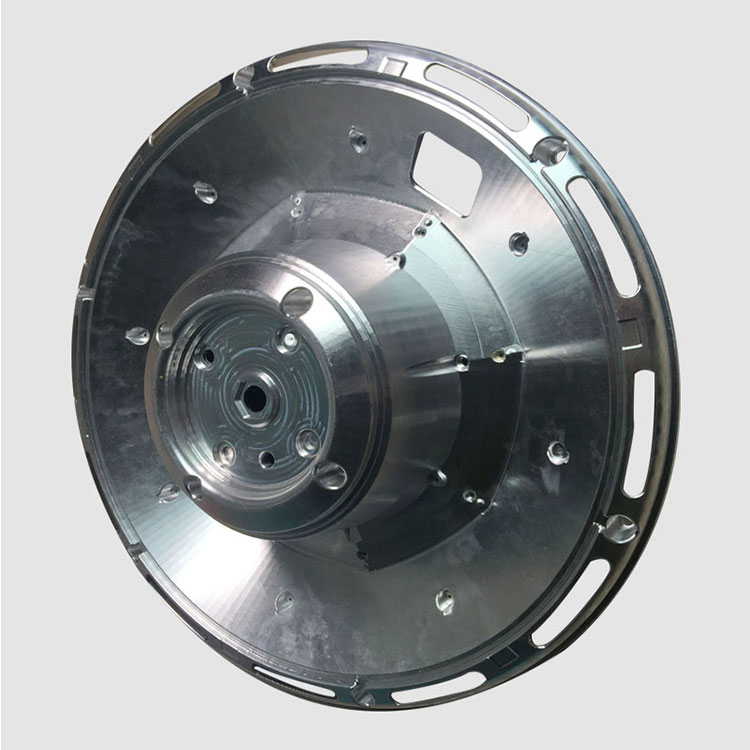
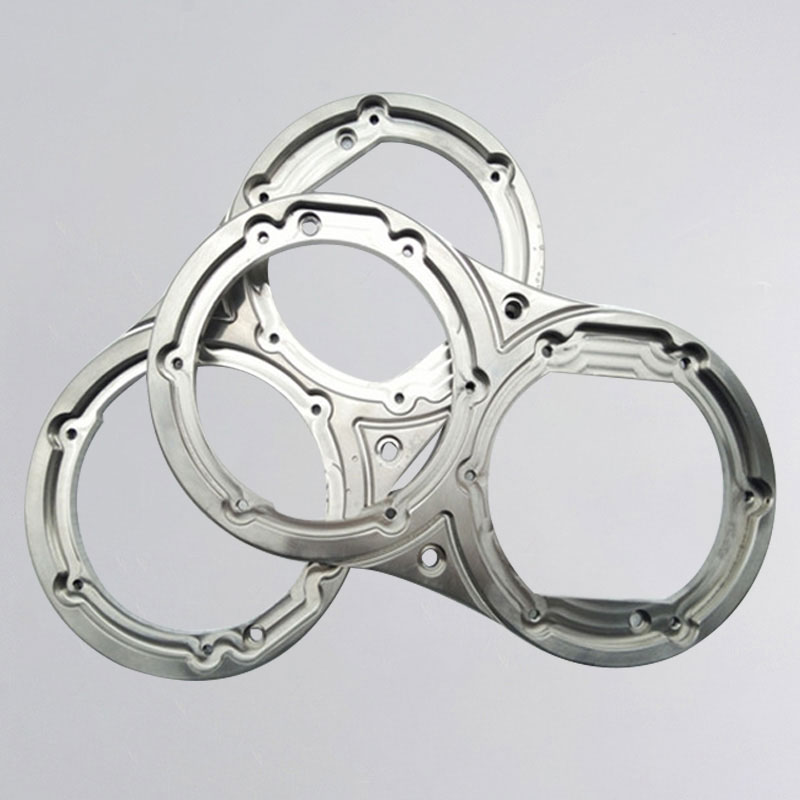
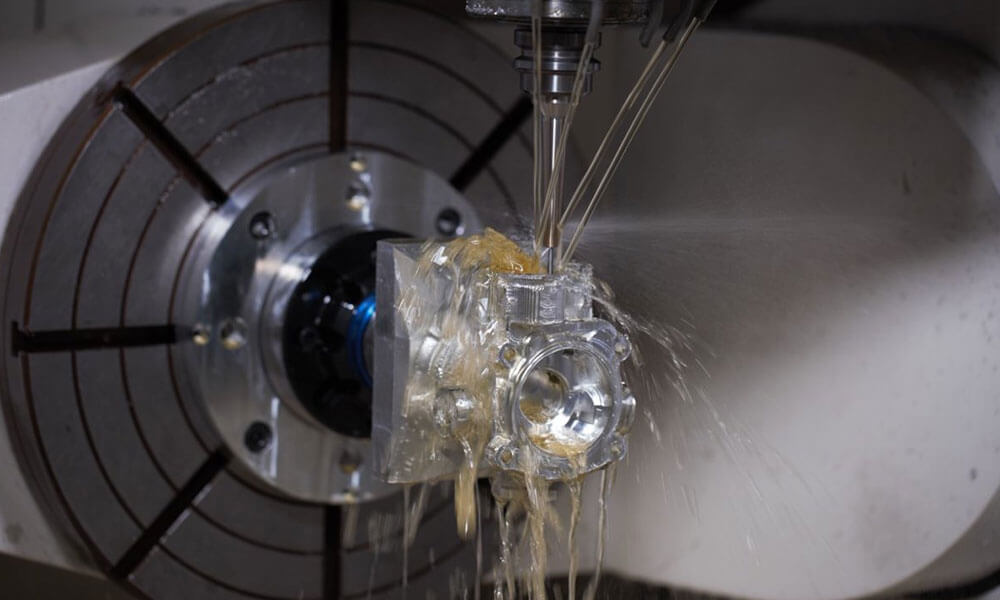
CNC Machining Company from China
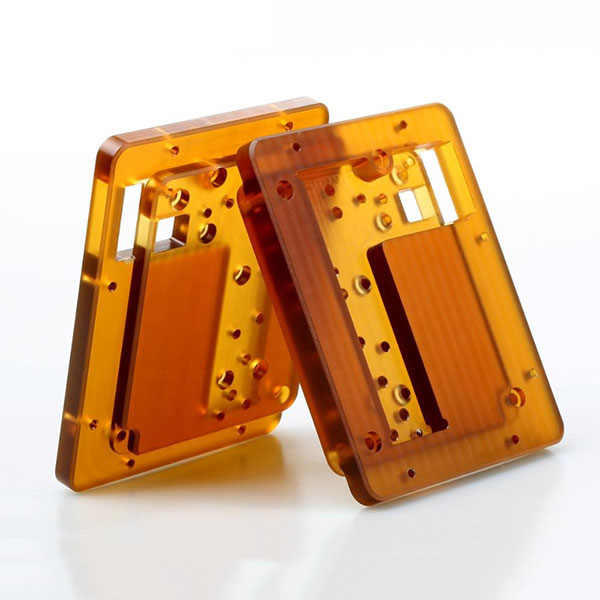
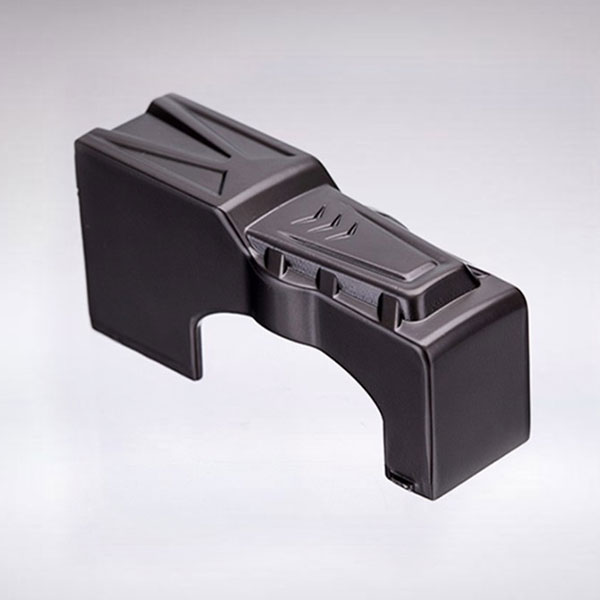
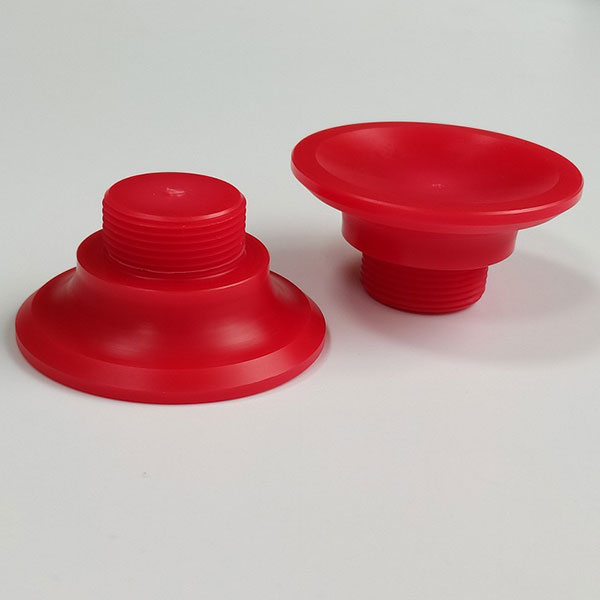
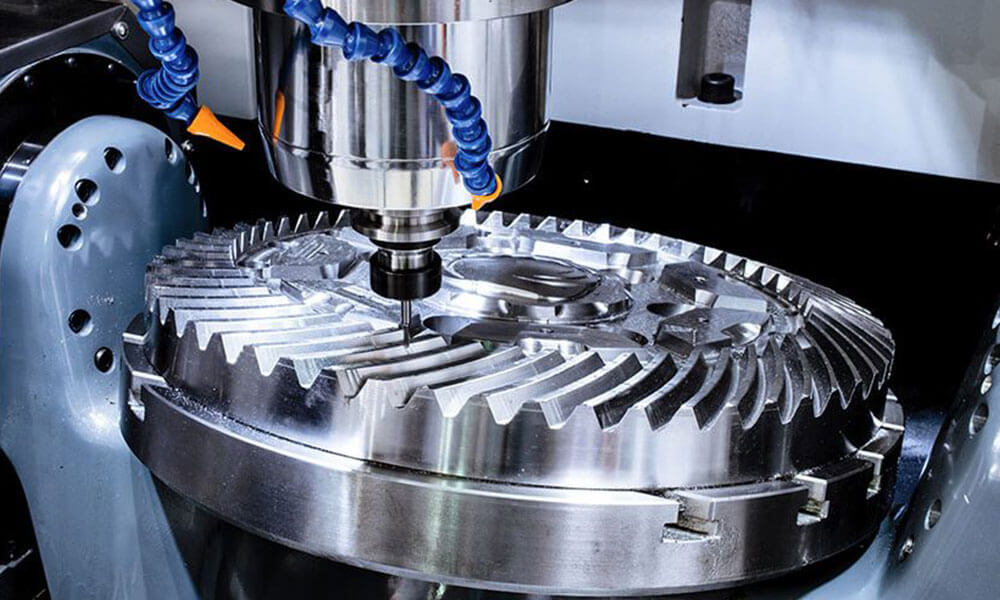
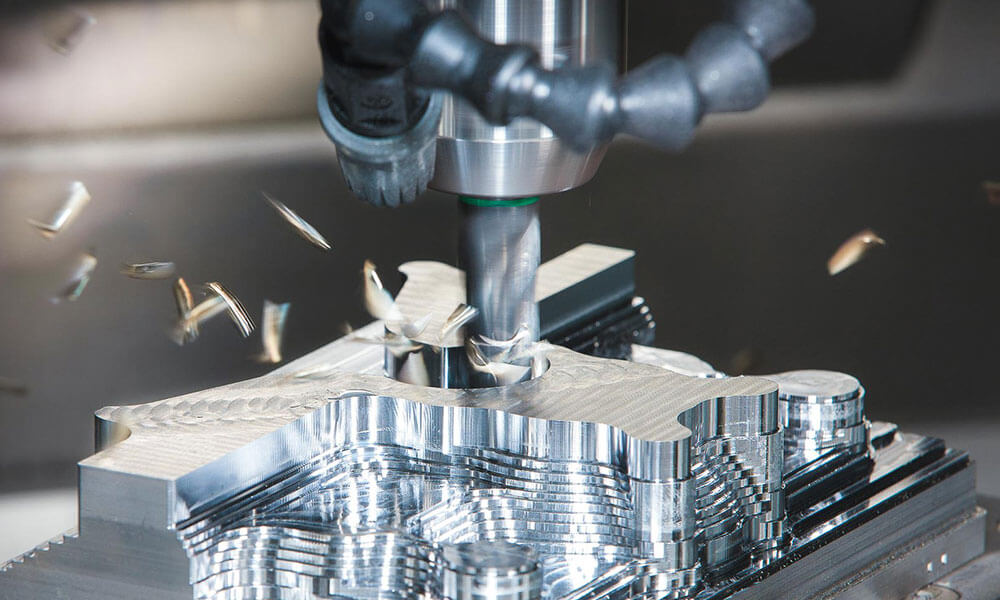
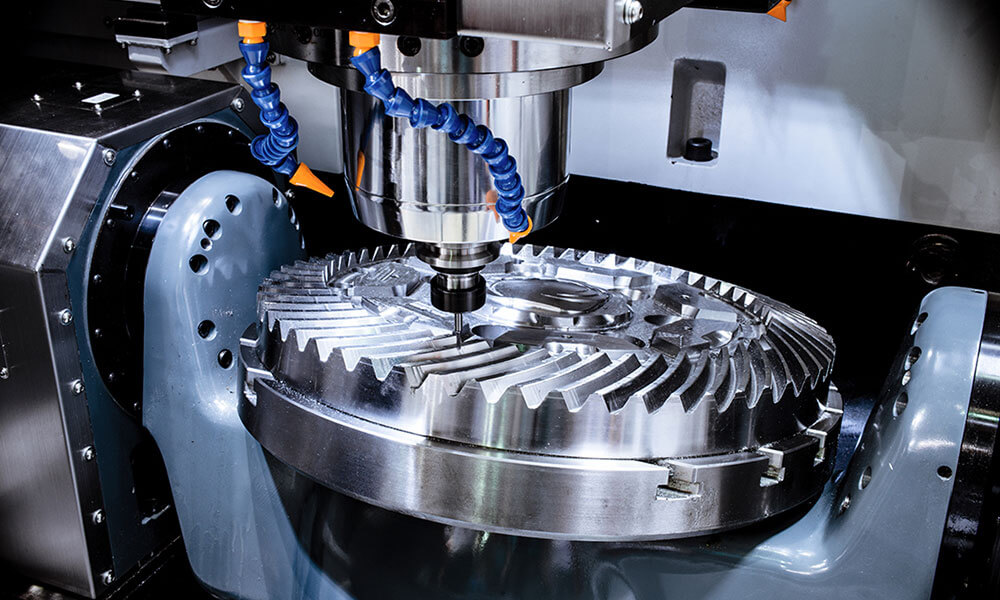
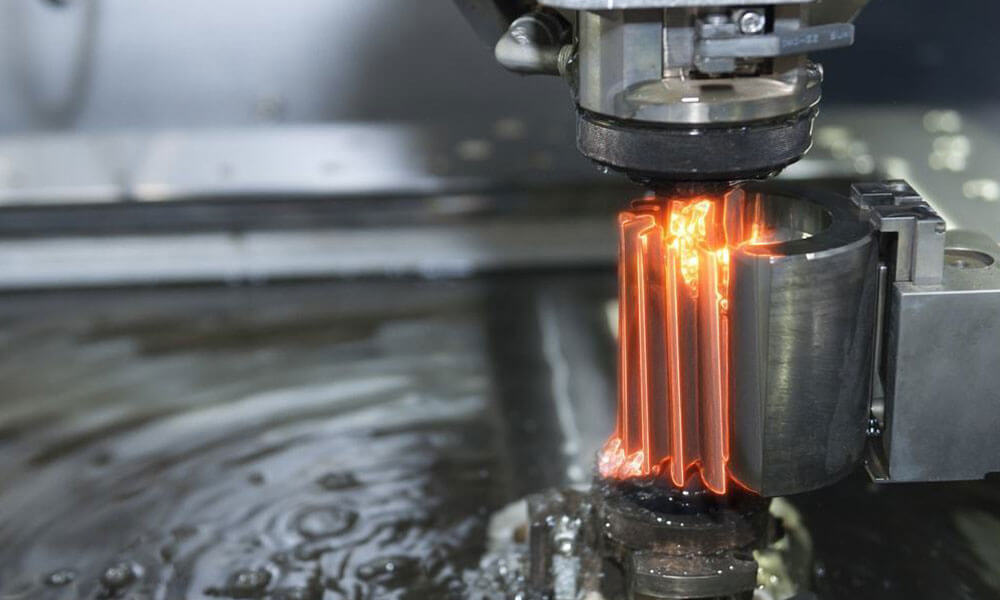
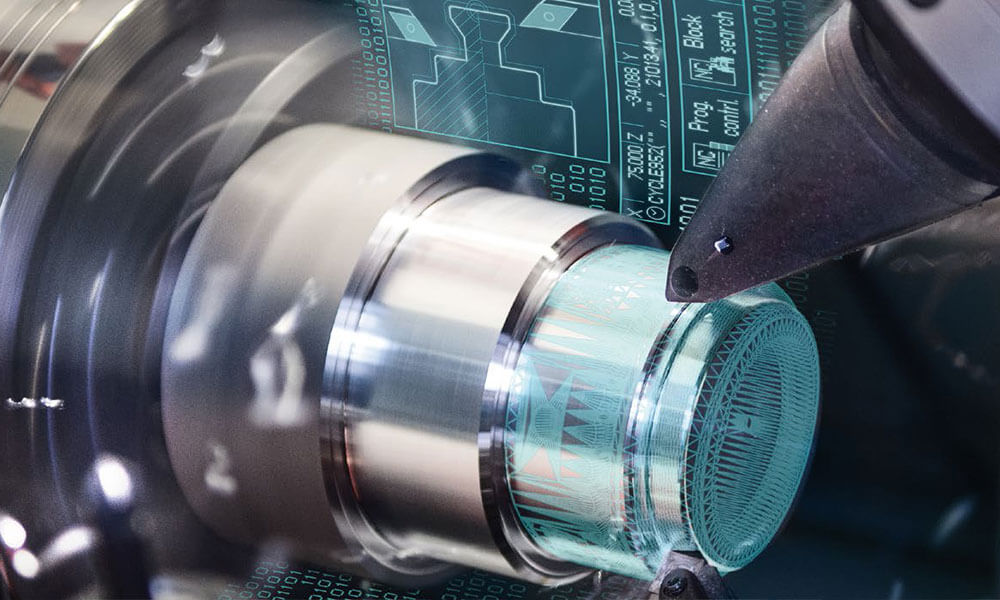
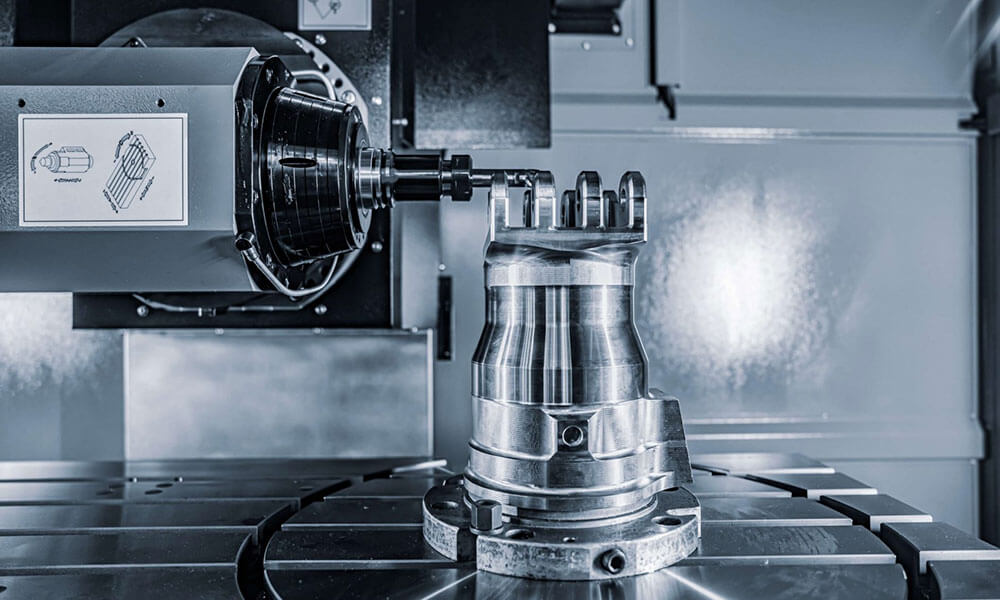
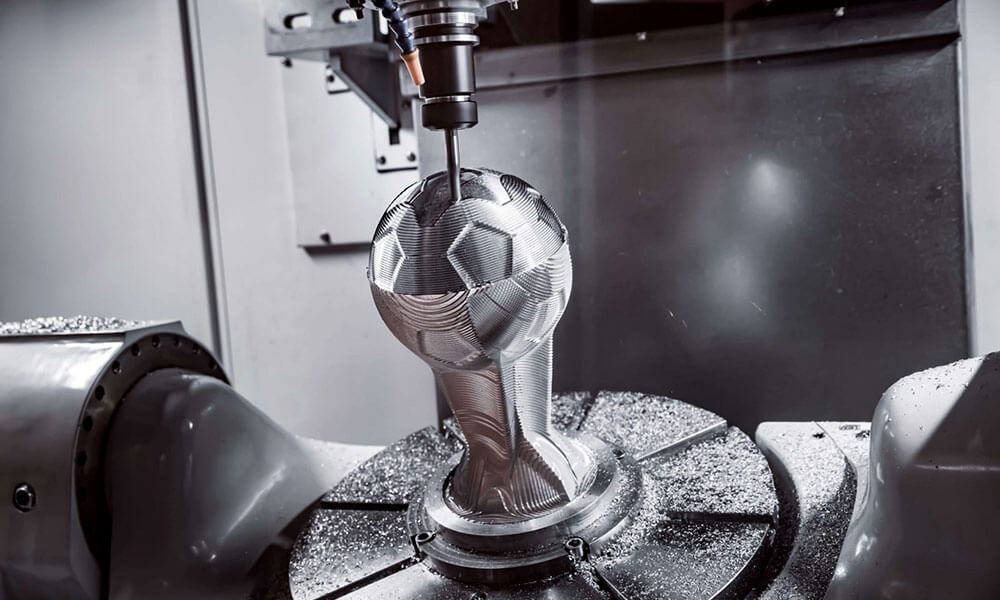
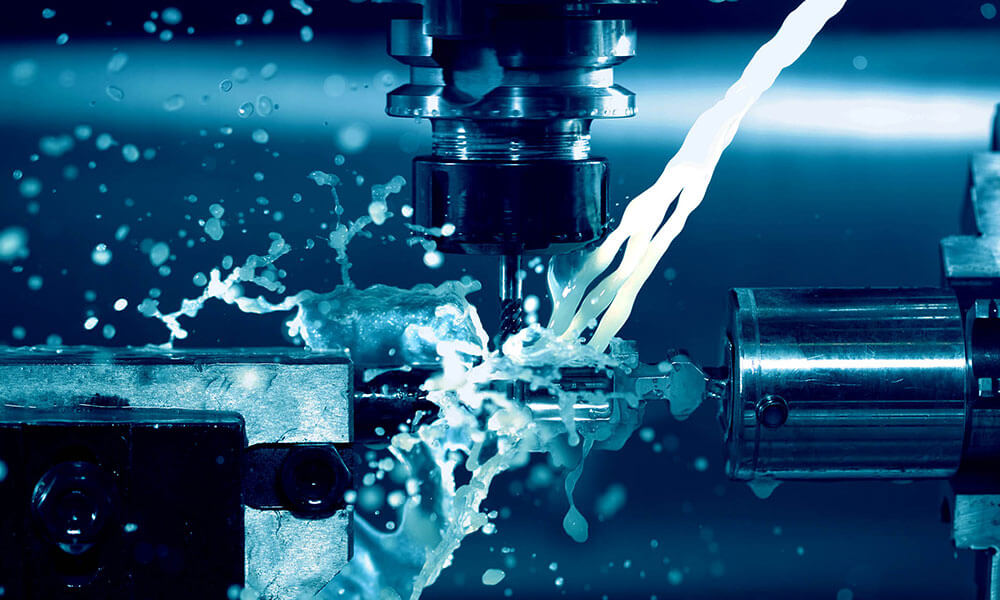
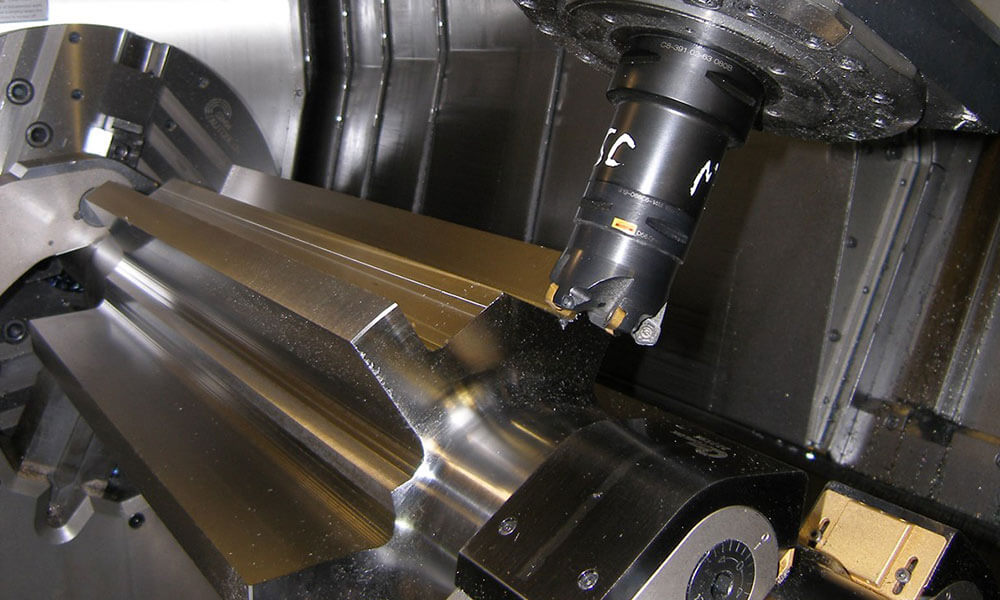
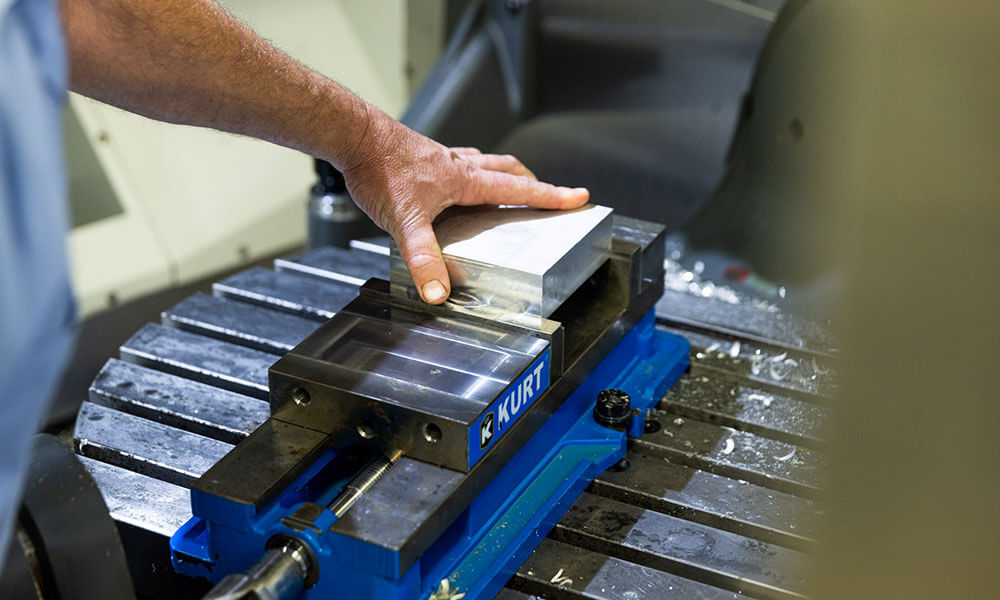
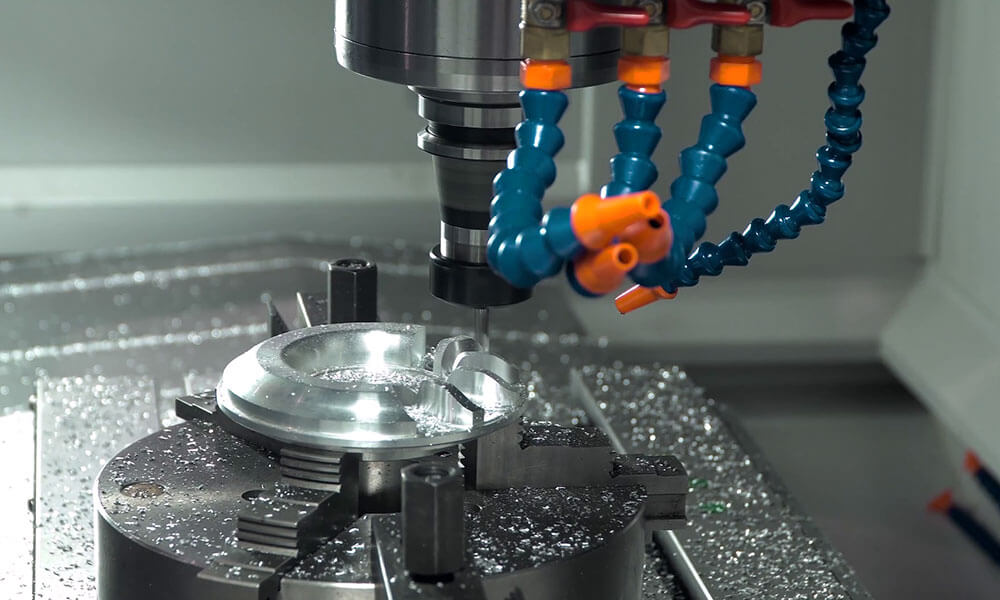
Holly provides high-precision CNC machining solutions tailored for industries such as automotive, electronics, medical, and industrial equipment. Whether you need rapid prototyping or mass production, our advanced 3-axis, 4-axis, and 5-axis CNC milling, CNC turning, drilling, and EDM machining ensure ±0.01 mm accuracy and superior quality.
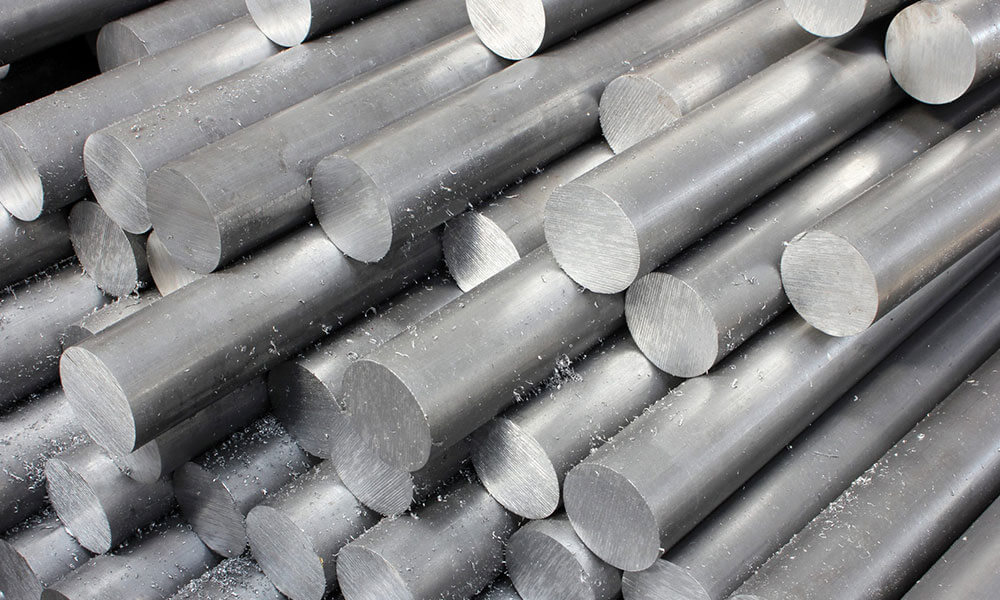
With a strong manufacturing network and advanced production capabilities, we work with a variety of materials, including aluminum, stainless steel, brass, and plastics, offering multiple surface finishing options to meet diverse requirements. Our ISO-certified processes and strict quality control ensure high performance and durability.
At Holly, we are committed to delivering cost-effective, high-quality CNC machined parts with fast turnaround times, supporting both small-batch and high-volume production. Contact us today to experience reliable and efficient CNC machining solutions!
Explore Our CNC Machining Technologies
Holly Plastic provides comprehensive CNC machining solutions with advanced CNC milling, CNC turning, EDM, and high-precision machining. Our facilities ensure ±0.01 mm accuracy across aluminum, stainless steel, brass, plastics, and more. We offer rapid prototyping, mass production, and diverse surface finishing options to meet various industry needs. With efficient production lines and strict quality control, we deliver cost-effective, high-quality custom parts with fast turnaround times.

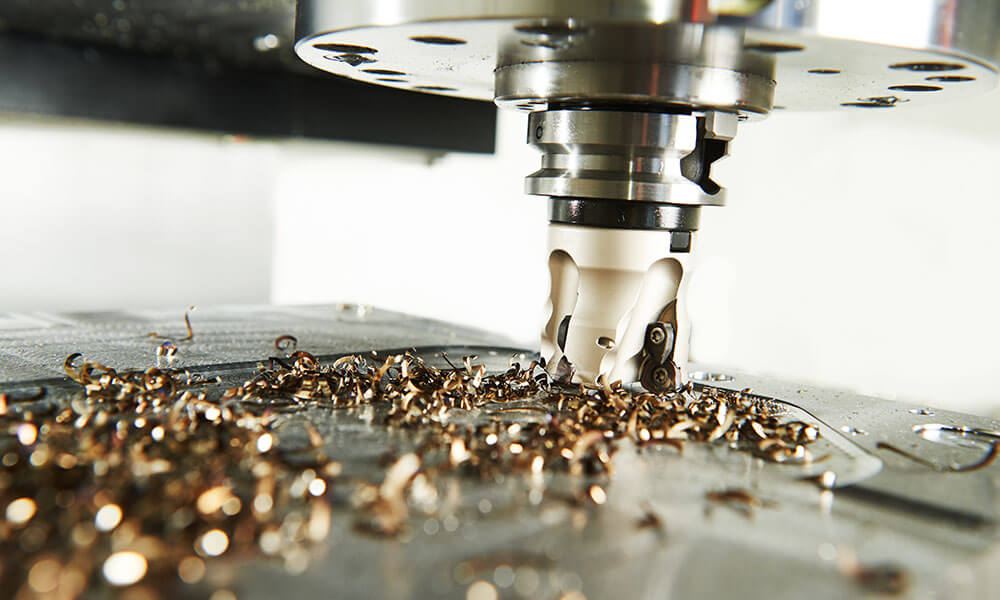
CNC Milling

CNC Turning

CNC Wire EDM

CNC Grinding
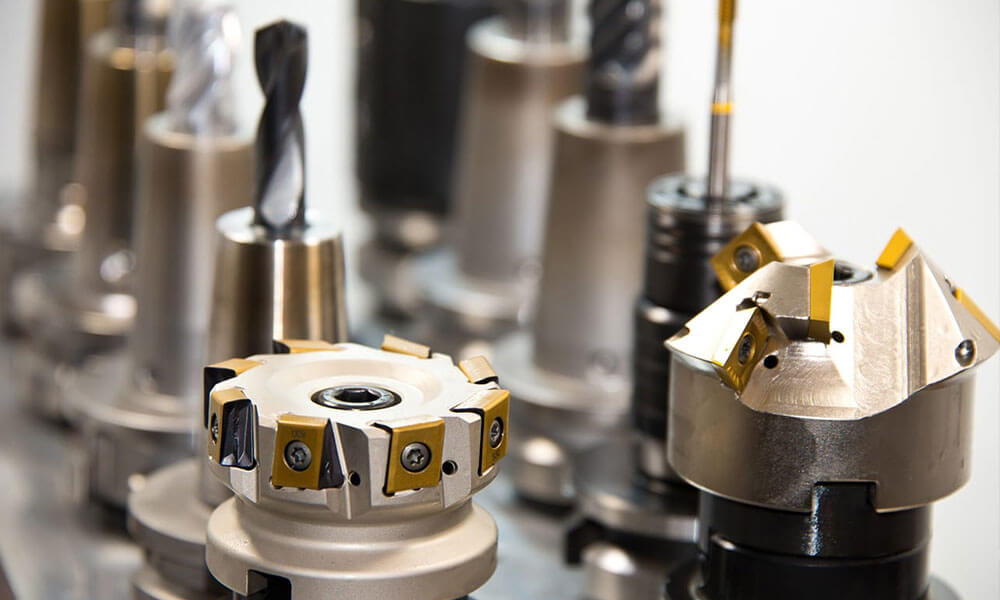
Our CNC Machining Capabilities
CNC Machining Materials Available
| Aluminum
Aluminum is a lightweight, durable metal commonly used in CNC machining due to its excellent machinability, corrosion resistance, and thermal conductivity. Popular grades include 6061, 7075, 5052, and 2024, each offering unique strength and hardness. Aluminum is widely utilized in aerospace, automotive, and electronics industries for high-performance components. It can be anodized for improved surface hardness and aesthetics. Its high strength-to-weight ratio and affordability make it a preferred material for precision machining.
|
 |
| Stainless Steel
Stainless Steel is a strong, corrosion-resistant metal widely used in CNC machining for its durability, heat resistance, and excellent mechanical properties. Common grades include 304, 316, 420, and 17-4 PH, each offering varying levels of strength and corrosion resistance. It is ideal for medical, aerospace, automotive, and industrial applications, where high strength and longevity are essential. Stainless steel can be polished or passivated for enhanced surface finish and protection. Its high wear resistance makes it a preferred material for precision-machined components.
|
 |
| Carbon Steel
Carbon Steel is a strong, durable metal widely used in CNC machining for its high strength, toughness, and cost-effectiveness. Common grades include 1018, 1045, and 4140, each offering varying levels of hardness and machinability. It is ideal for automotive, industrial, and structural applications, where high strength and wear resistance are essential. Carbon steel can be heat-treated for improved hardness and durability. While prone to corrosion, it can be coated or plated for added protection. Its affordability and versatility make it a popular choice for precision-machined components.
|
 |
| Copper & Brass
Copper & Brass are excellent choices for CNC machining due to their high machinability, excellent electrical and thermal conductivity, and corrosion resistance. Copper is widely used in electrical components (e.g., connectors, and heat sinks), while brass is favored for precision fittings (e.g., valves, gears, and decorative hardware) due to its low friction and antimicrobial properties. Their ability to achieve fine details and smooth finishes makes them ideal for electronics, plumbing, and industrial applications.
|
 |
| Titanium
Titanium is a lightweight, high-strength metal widely used in CNC machining for its exceptional strength-to-weight ratio, corrosion resistance, and biocompatibility. Common grades include Grade 2 and Ti-6Al-4V (Grade 5), offering varying levels of strength and durability. It is ideal for aerospace, medical, and high-performance automotive applications, where extreme strength and low weight are crucial. Though more challenging to machine, titanium delivers superior performance and longevity. Its natural resistance to heat and chemicals makes it a premium choice for demanding environments.
|
 |
| ABS
ABS is a versatile and durable thermoplastic widely used in CNC machining for its impact resistance, toughness, and ease of machining. It offers good heat and chemical resistance, making it ideal for automotive, consumer electronics, and industrial applications. ABS is lightweight, cost-effective, and supports various post-processing options such as painting, plating, and gluing. It is commonly used for prototypes, housings, and structural components where durability and aesthetics are important.
|
 |
| POM
POM (Polyoxymethylene), also known as Delrin, is a high-strength engineering thermoplastic widely used in CNC machining for its excellent wear resistance, low friction, and high stiffness. It offers great dimensional stability and chemical resistance, making it ideal for gears, bearings, bushings, and automotive components. POM has a naturally smooth surface, reducing the need for additional finishing. Its self-lubricating properties make it a top choice for applications requiring low friction and high durability.
|
 |
| PMMA
PMMA (Polymethyl Methacrylate), also known as Acrylic, is a transparent thermoplastic widely used in CNC machining for its high optical clarity, weather resistance, and lightweight properties. It offers good impact strength, UV resistance, and scratch resistance, making it ideal for display panels, light covers, lenses, and signage. PMMA can be polished to achieve a glass-like finish, making it a preferred choice for aesthetic and functional applications requiring transparency and durability.
|
 |
| Nylon
Nylon is a strong, wear-resistant thermoplastic widely used in CNC machining for its high toughness, low friction, and excellent chemical resistance. It offers good impact strength, heat resistance, and self-lubricating properties, making it ideal for gears, bearings, bushings, and structural components. Nylon is lightweight and absorbs minimal moisture, ensuring dimensional stability in demanding environments. It can be reinforced with additives like glass fiber for enhanced strength and rigidity, making it suitable for both industrial and mechanical applications.
|
 |
| PTFE
PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene), commonly known as Teflon, is a high-performance thermoplastic widely used in CNC machining for its exceptional chemical resistance, low friction, and high-temperature stability. It offers excellent electrical insulation, non-stick properties, and UV resistance, making it ideal for seals, gaskets, bearings, and medical components. PTFE is self-lubricating and can withstand extreme environments, making it a preferred choice for industrial, aerospace, and chemical applications requiring durability and low wear.
|
 |
| PEEK
PEEK (Polyether Ether Ketone) is a high-performance thermoplastic widely used in CNC machining for its exceptional strength, heat resistance, and chemical stability. It offers superior mechanical properties, excellent wear resistance, and biocompatibility, making it ideal for aerospace, medical, automotive, and industrial applications. PEEK maintains its structural integrity in extreme temperatures and harsh environments, making it a top choice for high-stress and precision components. It can also be reinforced with glass or carbon fiber for enhanced performance.
|
 |
| CFRP
Carbon Fiber Reinforced Polymer (CFRP) is a high-strength, lightweight composite material widely used in CNC machining for its exceptional stiffness, durability, and resistance to corrosion and heat. It offers a superior strength-to-weight ratio, making it ideal for aerospace, automotive, robotics, and sports equipment. CFRP is highly resistant to fatigue and deformation, ensuring long-term performance in high-stress environments. Its matte black finish and sleek aesthetics make it a preferred choice for both structural and aesthetic applications.
|
 |
| GFRP
Glass Fiber Reinforced Polymer (GFRP) is a strong, lightweight composite material widely used in CNC machining for its high tensile strength, corrosion resistance, and thermal stability. It offers excellent impact resistance and dimensional stability, making it ideal for automotive, aerospace, construction, and industrial applications. GFRP is more cost-effective than carbon fiber while still providing high durability and rigidity. Its electrical insulation properties make it suitable for electronic enclosures and structural components.
|
 |
CNC Machining Finishing Options
| Name | Description |
|---|---|

As-Machined |
No additional finishing; visible tool marks remain. Surface roughness typically Ra 1.6 – 3.2 μm. |
|
Polishing |
Smooths out surface roughness, improving aesthetics and texture. Used for metals and plastics. |

Bead Blasting & Sandblasting |
Uses high-speed blasting of glass beads or sand to create a uniform matte or satin finish. |

Anodizing, Type II & Type III |
Forms an oxide layer on aluminum to enhance corrosion resistance and appearance. Type III offers better hardness. |

Plating |
Metal plating (nickel, chrome, zinc) enhances corrosion resistance, wear resistance, or conductivity. |

Black Oxide |
Applies a black oxide layer to steel parts for mild corrosion resistance without affecting dimensions. |
| Powder Coating | Electrostatically applies a durable, colored powder coating that is heat-cured for enhanced protection. |
| Electropolishing | Electrochemical process that removes micro-imperfections, enhancing corrosion resistance and brightness. |
| Laser Engraving/Marking | Uses lasers to create durable markings for branding, serial numbers, and identification without affecting coatings. |
| Custom Coatings | Specialized coatings such as Teflon, ceramic, or custom chemical-resistant finishes for specific applications. |
Small Batch CNC Machining FAQ
CNC Machining FAQ Guide
In the following guide, you will know everything about CNC Machining Service.
CNC machining can be a good choice of prototype, but its applicability depends on the nature of the prototype. What is the purpose of the prototype? What material is it made of? What material is the last part made of? All these questions will ultimately lead users to find the most suitable prototyping method.
1. What is CNC machining?
Computer Numeric Controlled (Computer Numeric Controlled) processing is the use of CNC machine tools to process metals and plastics, as well as index-controlled processing tools. CNC refers to the programming and control of CNC machine tools with CNC machining language (usually called G code). The G code language of CNC machining tells the Cartesian coordinate position of the CNC machine tool, controls the feed speed and spindle speed of the tool, and functions such as tool changer and coolant.
2. What are the advantages of CNC machining?
Here are some advantages of CNC machining.
1) The number of matching molds is greatly reduced, and complex matching molds are not required to process parts with complex shapes. If you want to change the shape and size of the part, you only need to modify the processing procedure of the part, which is suitable for the development and modification of new products.
2) In terms of processing quality, accuracy, and repeatability, the aircraft-specific requirements can be met with the equipment.
3) Multivariety and small-batch production are more efficient because they can reduce the time it takes to prepare production, adjust machinery, and perform process inspections, and they can use the best cutting amount to reduce the cutting time.
4) It can process complex profiles that are difficult to process by traditional methods, and even process some invisible processed parts.
3. What are the characteristics of CNC machining?
For CNC machining, it has the following 5 characteristics for your reference.
1) High processing precision and stable quality.
2) High production efficiency.
3) Strong adaptability to processing various objects, such as small parts, complex parts with high precision requirements, expensive parts that are not allowed to waste, and parts with the shortest production time.
4) High level of automation and low labor intensity.
5) Facilitate the realization of modern management.
4. How many types of CNC machine tools are there?
CNC machining machines are designed to manufacture a wide variety of objects. In this case, there are a variety of commonly used CNC machining machines.
1) CNC milling machine
It is one of the most common types of CNC machine tools. CNC milling machines cut various materials under computer control. The CNC milling machine can translate specific numerical and letter programs and move the spindle in different ways.
2) Computer numerical control lathe
The function of the CNC lathe is to cut while the workpiece is rotating. CNC lathes can use different types of tools for precise and fast cutting. Compared with manual lathes, these CNC machine tools are excellent in terms of accuracy. They usually have fewer axes than CNC milling machines, so they are smaller and more compact.
3) CNC router
The CNC router is a machine used to cut various materials, very similar to the commonly used handheld routers. This type of CNC machine tool can help cut steel, wood, aluminium, composite materials, plastics and foam. CNC routers work similarly to CNC milling machines. It can use the computer numerical control function to control the running path of the router. Compared with other machines, CNC routers can produce different products in a shorter time, thereby reducing waste and increasing productivity.
4) CNC plasma cutting machine
The process of a CNC plasma cutting machine involves the use of a plasma torch to cut materials. Steel and other heavy metals are usually cut using this method.
5) CNC EDM machine tools
Electrical discharge machining (EDM) involves the use of electrical discharge or sparks in a specific material to create a specific shape.
6) CNC laser cutting machine
A CNC laser cutting machine is similar to a CNC plasma machine tool. The only difference between them is that the laser is mainly used for cutting, and it is great when it comes to cutting metal, plastic or hardwood. The intensity of the laser can be adjusted according to the density and intensity of the material.
5. What types of materials can be used for CNC machining?
A variety of materials can be machined using CNC machining, including aluminium alloys, brass, copper, steel, plastic, titanium, and others.
1) Aluminum alloy
Aluminium alloy has low density but relatively high strength, close to or exceeds that of high-quality steel, good plasticity, can be processed into various shapes, has excellent electrical conductivity, thermal conductivity and corrosion resistance, and is widely used in the industry compared with steel.
Some aluminium alloys can obtain excellent mechanical properties, physical properties and corrosion resistance after heat treatment. Aluminium alloys that incorporate a small amount of copper and magnesium are called hard aluminium alloys. They have high hardness, but low plasticity.
The super aluminium alloy Al-1-Al-Al-O system can be strengthened after heat treatment. It is the highest strength aluminium alloy at room temperature, but it has poor corrosion resistance and softens quickly at high temperatures. Wrought aluminium alloy is mainly an alloy of aluminium-aluminium alloy. It has a variety of elements, less content, good thermoplasticity, and is suitable for forging.
Aluminium alloy has excellent processing performance, welding performance, corrosion resistance, toughness, high toughness, no deformation, compact material, no defects, easy polishing film, oxidation effect and other excellent properties. Scope of application: building windows, curtain walls, industrial equipment, frame accessories, solar energy frames, etc.
Commonly used models are: AL6061, Al6063, AL6082, AL7075, AL5052, A380.
2) Brass
There are two types of brass: ordinary brass and special brass. Brass has good plasticity and corrosion resistance, good deformability and casting properties, and has strong application value in the industry. According to the different chemical compositions, brass can be divided into two categories: ordinary brass and special brass. The so-called ordinary brass is a binary alloy of copper and zinc.
Among brasses, there are everyday brasses and special brasses. In order to obtain higher strength, corrosion resistance and good casting performance, aluminium, iron, silicon, manganese, nickel and other elements are added to the copper-zinc alloy. Therefore, copper alloys composed of two or more elements are called special brass.
Ordinary brass is composed of copper and zinc. According to the difference in zinc content, it can be divided into single-phase brass and dual-phase brass, but the zinc content cannot exceed 45%, otherwise, the material will become brittle and cannot be used.
Special brass: The multi-component alloy formed by adding other alloying elements to ordinary brass is called brass. The frequently added elements include lead, tin, aluminium, etc., which can be called lead brass, tin brass, and aluminium brass. The purpose of adding alloying elements. Its main purpose is to increase tensile strength and improve processing performance.
Common types are: HPb63, HPb62, HPb61, HPb59, H59, H68, H80, H90.
3) Copper
It is also called red copper or pure copper. Due to its excellent electrical and thermal conductivity, copper is widely used in the electrical industry and precision processing industries. The biggest advantage and performance of copper is its good electrical conductivity, second only to silver, but the price of copper is much cheaper than silver. The electrical industry has become reliant on red copper.
High-purity copper is the primary condition for use in the electrical industry, and the purity must be higher than 99.95%. As long as a very small amount of impurities are mixed, the conductivity of the product copper will be greatly reduced, and the oxygen content of copper will also have a great influence on the conductivity. Mainly avoid the following impurities: phosphorus, arsenic, aluminium, lead, antimony, etc. This kind of high-purity copper can only be obtained by electrolysis using original copper as the positive electrode, pure copper as the negative electrode, and sulfuric acid solution as the electrolyte. During the electrolysis process, the original copper on the positive electrode is melted and ionized, and pure copper ions are adsorbed on the negative electrode to obtain the pure copper we need.
Purposes of copper: wires, cables, brushes, EDM copper, generators, bus bars, switch cabinets, transformers, heat exchangers, pipelines, flat plate collectors for solar heating devices, etc.
Common ones are: C11000, C12000, C12000, C26000, C51000.
4) Steel
Steel is an iron-carbon alloy. We usually call it steel. In order to ensure its toughness and shape, the carbon element does not exceed 1.7%. In addition to iron and carbon, other elements of steel include silicon, manganese, sulfur, and phosphorus. Other components will make the steel performance different.
Both steel and iron are iron-based iron-carbon alloys, but due to the difference in carbon content, the state and structure of iron-carbon alloys are also different at different temperatures. Iron has poor formability, is not easy to deform, and has poor weldability. These properties of steel are excellent, especially when a certain amount of alloying elements are added to steel, there will be some special properties, such as high strength, wear resistance, heat resistance, and corrosion resistance.
After ordinary steel is refined and other alloying elements are added, widely used steels with different properties can be produced, such as fatigue resistance, heat resistance, impact resistance, wear resistance, corrosion resistance, high polishing, etc. These high-quality steels are widely used in machinery parts, injection mold steel, stamping mold steel, aerospace, tools, automobiles, home appliances and other industries.
In order to improve the performance of steel, we usually use heat treatment, stress treatment, quenching and tempering treatment, surface coating and other methods.
5) Plastic
Plastic is a polymer, and its main component is a synthetic resin. In addition, add some specific purpose additives as needed, such as plasticizers that can improve plasticity, anti-ageing agents that prevent plastics from ageing, and so on.
Although the relative molecular weight of the polymer is large, its composition is not complicated and its structure has certain rules. They are made by the polymerization of small molecules, such as polyethene plastics, which are made by the polymerization of ethylene molecules. When polyethene plastic is heated to a certain temperature range, it starts to soften until it melts into a flowing liquid. The melted polyethene plastic becomes solid after cooling and then melts into liquid after heating. This phenomenon is called thermoplasticity.
Polyethene, polyvinyl chloride and polypropylene are all thermoplastics. Some plastics can be softened and moulded into a certain shape only when heated in the manufacturing process, and will no longer be heated to melt after processing and have thermosetting properties, such as phenolic resin.
Plastic is a poor conductor of heat, which has the effect of silencing and damping. Plastic hardness, tensile strength, elongation and impact strength. Due to its small specific gravity and high strength, plastic has high specific strength.
Plastic parts are widely used in various fields of life, such as household appliances, instrumentation, wires and cables, construction equipment, communication electronics, automotive industry, aerospace, daily hardware, etc.
Commonly used plastics are ABS, PC, PE, POM, Delrin, nylon, Teflon, PP, PEI, Peek, carbon fiber.
6) Titanium
Our commonly used titanium alloys are composed of titanium, aluminium, tin, vanadium, and niobium, and different elements form different properties.
The main excellent characteristics of titanium are described as follows:
- Low density and high specific strength: Titanium has a higher density than aluminium, but is lower than steel, copper and nickel, but the strength is on top of the metal.
- Good corrosion resistance and heat resistance. It is possible to use the titanium alloy at a temperature of 600°C for a long time.
- Low-temperature resistance: Titanium alloys Ti-al-2, Ti- 2-o and Ti alloys are low-temperature titanium alloys, whose strength increases with decreasing temperature, but the plasticity changes little. It maintains good plasticity and toughness at a low temperature of 196-253℃, avoids the cold brittleness of metals, and is an ideal material for cryogenic containers and storage tanks.
- The tensile strength is close to its yield strength: the titanium material has a higher yield strength ratio (tensile strength/yield strength) during the forming process, indicating that its plastic deformation is poor. Due to the large ratio of the yield limit to the modulus of elasticity of titanium, the forming of titanium can have great elasticity.
- Better heat transfer performance: Although the thermal conductivity of titanium is lower than that of carbon steel and copper because titanium has excellent corrosion resistance, the thickness can be greatly reduced, and the surface heat resistance and steam reduce the thermal resistance, so there is no junction on the surface. Adding a layer of fouling to titanium can improve heat transfer by significantly reducing thermal resistance.
Based on the above-mentioned excellent properties, titanium alloys are mainly used in aerospace, aviation industry, marine biomedicine, automotive industry and other fields.
Common types are Ti-1 and Ti-2.
6. Which finishing can be used for CNC machining parts?
Machining surface treatment is an important processing procedure in CNC machining, and it plays an important role in the protection and beautification of workpieces. Various types of surface treatment can be applied to CNC machining. During the processing, it is necessary to select the correct surface treatment type according to the material and processing requirements of the workpiece.
The surface treatment of CNC machined parts mainly includes polishing, electrostatic spraying, baking varnish, zinc plating, chrome plating, nickel plating, titanium plating, gold plating, silver plating, aluminium anodizing, dipping, paint, sandblasting, powder coating, DLC treatment, Teflon Dragon treatment, black oxidation, etc.
7. What is the polishing of CNC machined parts?
Polishing is the process of grinding and modifying the surface of parts using various tools and media. The purpose of polishing is to smooth the surface of a part, but it cannot improve dimensional accuracy or geometric accuracy. Technically speaking, polishing refers to the use of abrasives and machinery to make the surface of a part smooth, while using machinery to apply abrasives to the surface of loose parts is a more active process, which results in a smoother and brighter surface finish.
8. How many steps do the polishing of CNC machined parts need?
The polishing of CNC machined parts is generally divided into three steps:
In the first step, the surface after lathing, grinding, CNC, spark machine, wire cutting and other processes is generally rough and needs to be polished with oilstone.
The second step is sandpaper operation after the oilstone operation. When sandpaper operation, pay attention to the production of round edges, sharp corners, rounded corners, and orange peel of the parts.
In the third step, the diamond grinding paste is mainly used, and the accuracy requirements require a clean polishing chamber during the R0.2 polishing process.
9. How to apply CNC machining?
CNC machining is a multi-functional and cost-effective manufacturing process compatible with multiple materials. Therefore, it can be used in a variety of industries (including aerospace, automotive, medical, consumer goods, industrial, energy, furniture, electronics, etc.), for various applications, and can be used in different ways: Direct production process, indirect manufacturing process or a combination of other processes.
The unique advantages of CNC machining and the characteristics of CNC parts (high precision, short turnaround time, and good material quality), and even the advantages of being able to handle almost all materials, make its applications unlimited.
10. What machine Holly has CNC machining?
The company has 50 CNC milling machines, 1 MAKINO brand high-speed CNC milling machine, 5 electrode CNC milling machines and other types of CNC machining equipment.
11: What is the standard tolerance of CNC machined parts?
Generally, Holly manufactures CNC machined parts according to ISO 2768-1. “F” means processed steel and aluminium, “M” means processed plastic, and “C” means vacuum casting.
We can achieve tighter tolerances, but this depends on the geometry and material type of the part.
If you require stricter tolerances than the above ISO standards, you need to specify and negotiate during the quotation stage.
12. What is the minimum order quantity for your CNC machined parts?
We have no special inquiry about the quantity of CNC machined parts because Holly always welcomes you no matter the customer is big or small. The number of orders we can accept ranges from 1 to more than 100,000.
13. How to ensure the quality of CNC machined parts?
The company has passed ISO9001: 2015 quality system certification. In order to provide our customers with high-quality parts, we strictly abide by the ISO standard, from the income of raw materials to 100% inspection of every part delivered. We have complete testing equipment in the country, and our inspectors have been professionally trained before working independently.
14. How do I request a quotation (RFQ) for CNC machining?
For a better evaluation and analysis of RFQs of CNC machining projects, the following details are required.
Case 1: There are drawings of CNC machining parts.
- It is necessary to provide 2D and 3D files (DWG, PDF, JPG, dxf, etc.).2) Material type.
- Surface treatment.
- Quantity.
Situation 2: Samples can be provided for our reference, no parts drawings are required.
like the most. What is the best selling CNC machine tool?
There are various brands of CNC machine tools. Metal cutting machines are the most commonly used CNC machine tools with the highest market share, including CNC milling machines, CNC lathes, and tapping centres. Let’s share some of the best-selling brands.
- Dmg Sen
- German runner
- Germany STAMA
- Japanese Mori Seiki
- Okuma, Japan
- Yamazaki Mazak, Japan
- Japan Makino
- Japan Toyota
- German Magazine
- Hardinge
- Italy FIDIA
- Danobat, Spain
- American Haas
15. What are the steps for CNC machining?
Only by fully understanding the steps of CNC machining can the machining efficiency be better improved. Therefore, it is necessary to understand the steps of CNC machining.
1) Analyze the processing drawings and determine the processing technology.
According to the processing drawings provided by the customer, the operator can analyze the shape, dimensional accuracy, surface roughness, materials and heat treatment conditions of the parts. Then we can choose the appropriate machine tool and tool to determine the positioning and clamping device, the processing method, the processing sequence and the size of the cutting amount. When determining the processing technology, the command function of the CNC machine tool should be fully considered, and the efficiency of the machine tool should be given full play to make the processing route reasonable and the processing time short.
2) Calculate the coordinate value of the tool path reasonably.
According to the geometric size of the processed part and the coordinate system set by the program, the motion path of the tool path center is calculated to obtain all tool position data.
3) Input the part numerical control processing program.
Please pay attention to these two points when writing: One is the standardization of written procedures to facilitate expression and communication; second, we should be fully familiar with the performance and instructions of CNC machine tools.
16. What will affect the cost of CNC machined parts?
1) Material
Some materials are more difficult to process than others, and some materials are more expensive than raw materials, both of which increase processing costs.
2) Dimensions of CNC machined parts
There is no doubt that the size and overall geometry of the parts are important factors that affect the cost of CNC machining parts. Obviously, the larger the product, the more materials are needed. In addition, the more detailed and complex the geometric design, the higher the manufacturing cost.
3) Requirements for CNC machining and manufacturing equipment
The type and quantity of equipment also have an important influence on the cost of CNC machining.
4) Processing other than CNC machining
Additional processing is required for many CNC-machined products, such as heating, special processing, as well as surface treatment and professional coating. All of these will increase the total cost, so we should carefully evaluate whether it is necessary and worthwhile.
5) The price of working hours in the market
The location and environment of the factory will cause a big gap in working hours and labour costs.
17. How many factors affect the accuracy of CNC machining parts?
1) Mismatched position in CNC machine tool processing
Position mismatch refers to the amount of change or deviation between the actual surface, axis or symmetry plane of the processed part and its ideal position, such as perpendicularity, position, symmetry, etc. Usually, the position mismatch in CNC machine tool processing refers to the dead zone mismatch. The main reason for the position mismatch is the clearance and elastic deformation generated during the transmission of the machine tool parts during the machining process, and the machine tool head needs to overcome friction and other factors during the machining process.
2) Shape and position tolerance
In CNC machine tool processing, because the machine tool fixture is affected by external forces, the geometric accuracy of the machine tool is affected under the influence of external factors such as heat generated during the processing.
3) Machine positioning
Precision machining of CNC machine tools is greatly influenced by tool positioning. From a structural point of view, the machining errors of CNC machine tools are mainly caused by positioning accuracy. Among them, the machine tool feed system is the main link that affects the positioning accuracy. The feed system of CNC machine tools usually consists of two parts: mechanical transmission system and electrical control system. In the structural design, the positioning accuracy is related to the mechanical transmission system.
18. How do you guarantee the delivery time of CNC machined parts?
We all know that delivery time is the point that customers care about most. So how does Holly guarantee the delivery date of CNC machined parts?
Holly ensures that the same equipment can be used to process parts with the same precision, and risk management can be carried out in emergency situations. Especially for our mass-produced products, we strive for a stable supply through comprehensive production management to avoid delivery delays. Therefore, we always have two or more identical devices to manage risks in emergency situations. If there is a need for surface treatment, we also have professional partners to work closely with various processing requirements.
We operate the equipment 24 hours a day. For new projects, if you can provide drawings and CAD data, we will start and set up during the day. Due to the processing at night, the delivery time can be greatly shortened. In addition, we can also respond to the requirements of repeated CNC machining products within a short delivery time. By operating multiple CNC machine tools for 24-hour production, delivery time can be shortened.
19. What should we consider when choosing a CNC machining supplier?
When choosing a supplier for CNC machining, the following points should be noted.
- Maximize the public sharing of query information.
In CNC machining projects, public bidding is very important. Information release must ensure timeliness, so that suppliers have sufficient response time, and query results must be announced in a timely manner.
- Make the inquiry more attractive to qualified CNC machining suppliers.
- Don’t limit the number of suppliers to “three or more”.
- When choosing a supplier, low prices should not be the most important consideration.
- 1. What is CNC machining?
- 2. What are the advantages of CNC machining?
- 3. What are the characteristics of CNC machining?
- 4. How many types of CNC machine tools are there?
- 5. What types of materials can be used for CNC machining?
- 6. Which finishing can be used for CNC machining parts?
- 7. What is the polishing of CNC machined parts?
- 8. How many steps do the polishing of CNC machined parts need?
- 9. How to apply CNC machining?
- 10. What machine Holly has CNC machining?
- 11: What is the standard tolerance of CNC machined parts?
- 12. What is the minimum order quantity for your CNC machined parts?
- 13. How to ensure the quality of CNC machined parts?
- 14. How do I request a quotation (RFQ) for CNC machining?
- 15. What are the steps for CNC machining?
- 16. What will affect the cost of CNC machined parts?
- 17. How many factors affect the accuracy of CNC machining parts?
- 18. How do you guarantee the delivery time of CNC machined parts?
- 19. What should we consider when choosing a CNC machining supplier?