Injection molding is the overall manufacturing process of developing and producing the parts by injecting molten material into various molds. It usually can be divided into three types, plastic injection molding, metal injection molding, and powder injection molding.
The parts which are constructed or formed with the help of injection molding are very precise and accurate. Their design is very close to the ones required or as mentioned on the blueprints of any project. The process of injection molding can be conducted with a host of materials which mostly include glasses, metals, confections, elastomers, thermosetting polymers, and thermoplastics.
People use the injection molding technology in mass-production processes where the same part is being created thousands or even millions of times in succession.
1. Why Use Injection Molding?
The main advantage of injection molding is that it can be mass-produced. Once the initial cost is paid, the price per unit is very low during the injection molding manufacturing process. More and more parts are being transferred, and prices tend to fall sharply.
Besides, the rejection rate of injection molding is relatively low. Compared with the traditional manufacturing process, such as CNC machining, a large number of original plastic blocks or sheets are reduced. However, this may be a negative effect compared to additive manufacturing processes with lower scrap rates such as 3D printing.
Last but not at least important, injection molding is very repeatable. In other words, the second part you produce is actually the same as the first part. This is a good feature when trying to produce brand consistency and component reliability in mass production
2. How Does Injection Molding Work?
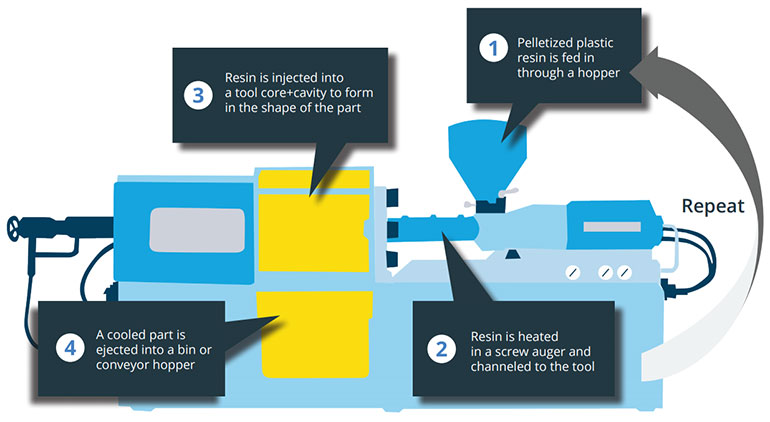
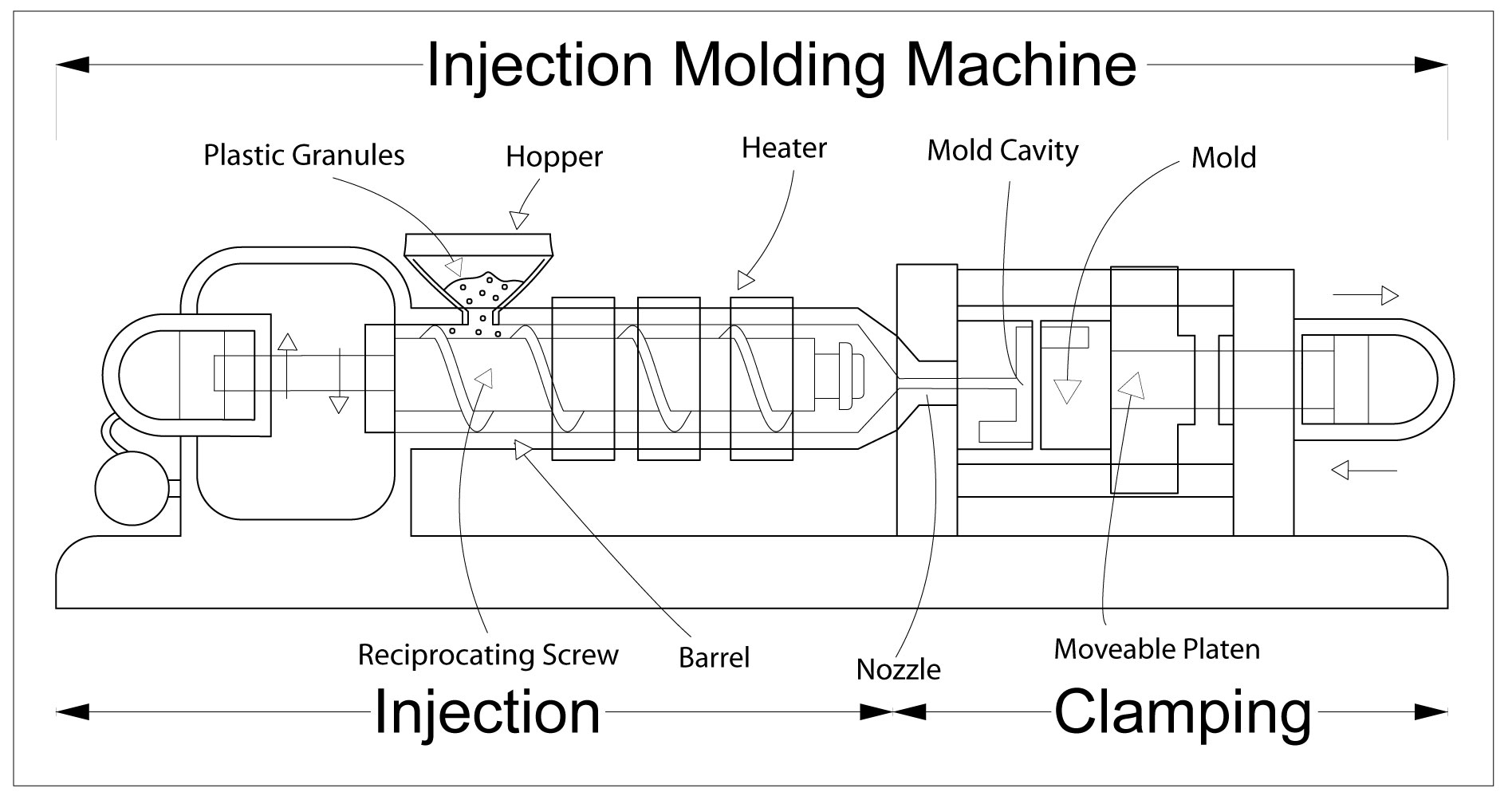
The injection molding machine is mainly composed of three parts: a feed hopper, a screw, and a heating barrel. It works by making plastic powder or granules into parts according to requirements and sizes
When the hopper receives plastic pellets, it uses the friction of the screw to generate heat. Once the plastic reaches the correct temperature, it is injected into the mold cavity, where it finally cools and forms a shape according to the mold design.
Advanced injection molding technology, like repeated injection, can use a variety of materials to make parts. Insert injection molding can also be used to add plastic parts to existing parts made of other materials.
3. Injection Molding Machine
There are different types of injection molding machines, such as m motorized machines driven by servo motors, hydraulic machines driven by hydraulic motors, and hybrid machines driven by a combination of a servo motor and a hydraulic motor.
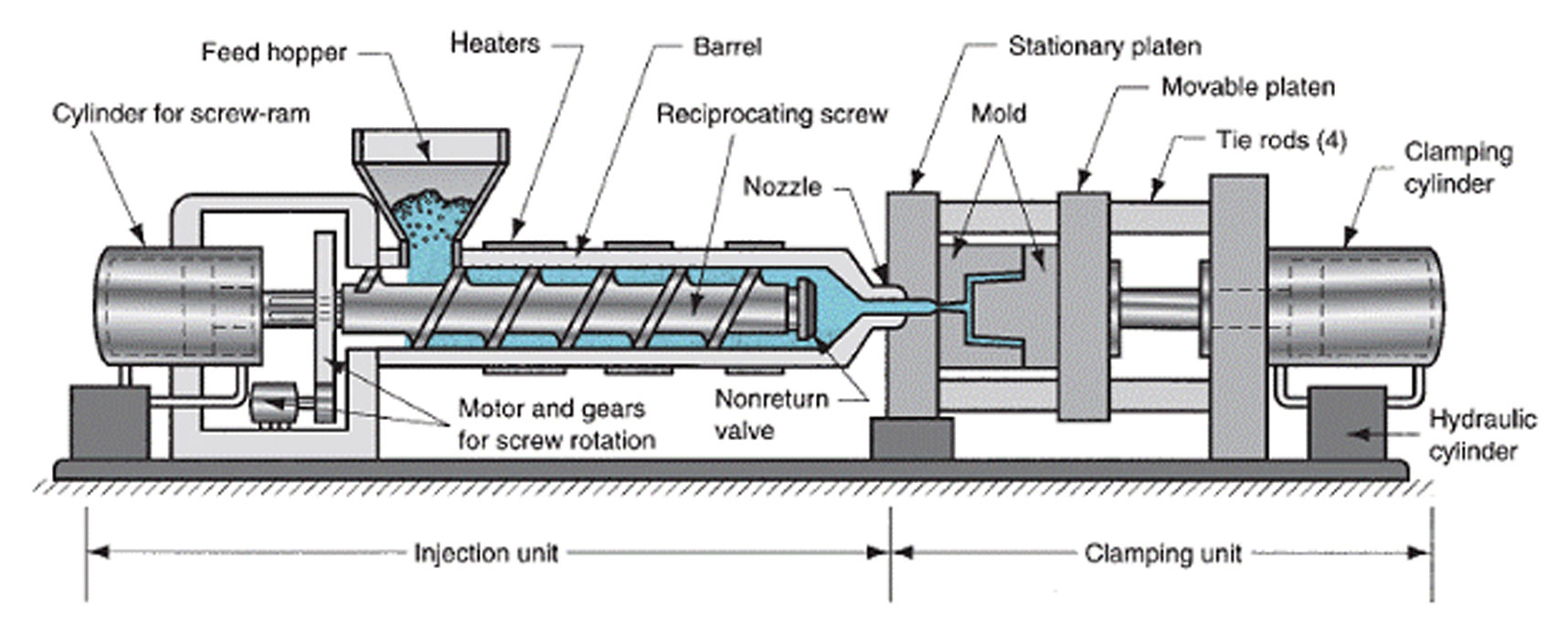
The structure of the injection molding machine can be simply summarized as an injection unit that sends the molten material into the mold and a clamping unit that operates the mold.
In recent years, the application of CNC has been increasingly used in injection molding machines, making models that achieve high-speed injection under program control becomes more and more popular. On the other hand, some specialized machines, such as the model that forms the light guide plate of the LCD monitors, are also used.
4. Injection Injection Molding Process
Injection molding starts with resin pellets (granules) being poured into the hopper, which is the entry point of the material. Then heat and melt the pellets in the cylinder to prepare for injection.
Then, the material is forced through the nozzle of the injection unit before being delivered through a channel called a sprue in the mold. and then into the mold cavity through a branch runner.
After the material cools and hardens, the mold opens and the molded part is ejected from the mold. In order to finish the molded part. Finally, the sprue and runner are trimmed from the part.
It is important that the molten material is evenly delivered to the entire mold, because there are usually multiple cavities in the mold, allowing multiple parts to be produced at the same time. Therefore, the design of the mold shape should ensure this.
While injection molding is suitable for mass production, it is necessary to have a good understanding of the various conditions required to produce high-precision products, including the selection of resin materials, the processing accuracy of the mold, and the temperature and speed of melt injection.
5. Considerations For Injection Molding
Before you try to produce a part by injection molding, consider the following things:
#1 Cost Considerations
Preparing a product for injection molding requires a large initial investment. You must understand this beforehand.
#2 Production Quantity
Determine the number of parts produced by injection molding as the most cost-effective manufacturing method. You should fix the number of production parts that you expect to break even on the investment. Considering the cost of design, testing, production, assembly, marketing, and distribution, and the expected price point for sales, you can build in a conservative margin.
#3 Design Considerations
You need to consider both part design and mold design in the early part designing stages. Simplifying the geometry and minimizing the number of parts will bring benefits to the road in the future. Besides, you need to make sure that the mold design can prevent defects in the production process.
#4 Production Considerations
You should reduce the cycle time as much as possible, small changes can make a big difference. When you produce millions of parts, shortening the production cycle by a few seconds can translate into huge savings. Using machines with hot runner technology or thoughtful tools will help a lot to shorten the cycle time.
On the other hand, designing your parts to reduce assembly will help you save a lot of labor costs. The reason why injection molding can be carried out in Southeast Asia is largely due to the cost of assembling simple parts in the injection molding process.
6. Conclusion
Injection molding is a great technique for the mass production of finished products. This is also useful for final prototypes for consumer or product testing. However, before this later stage of production, 3D printing is more affordable and flexible for designing early-stage products. You can combine different techniques to make your projects more successful.